Toxicity evaluation following intratracheal instillation of iron oxide in a silica matrix in rats
- PMID: 24949417
- PMCID: PMC4053145
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/134260
Toxicity evaluation following intratracheal instillation of iron oxide in a silica matrix in rats
Abstract
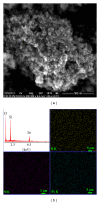
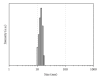
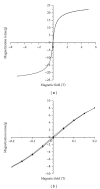
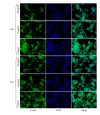
Iron oxide-silica nanoparticles (IOSi-NPs) were prepared from a mixture of ferrous chloride tetrahydrate and ferric chloride hexahydrate dropped into a silica xerogel composite. The structure and morphology of the synthesized maghemite nanoparticles into the silica xerogel were analysed by X-ray diffraction measurements, scanning electron microscopy equipped with an energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer, and transmission electron microscopy. The results of the EDAX analysis indicated that the embedded particles were iron oxide nanoparticles. The particle size of IOSi-NPs calculated from the XRD analysis was estimated at around 12.5 nm. The average size deduced from the particle size distribution is 13.7 ± 0.6 nm, which is in good agreement with XRD analysis. The biocompatibility of IOSi-NPs was assessed by cell viability and cytoskeleton analysis. Histopathology analysis was performed after 24 hours and 7 days, respectively, from the intratracheal instillation of a solution containing 0.5, 2.5, or 5 mg/kg IOSi-NPs. The pathological micrographs of lungs derived from rats collected after the intratracheal instillation with a solution containing 0.5 mg/kg and 2.5 mg/kg IOSi-NPs show that the lung has preserved the architecture of the control specimen with no significant differences. However, even at concentrations of 5 mg/kg, the effect of IOSi-NPS on the lungs was markedly reduced at 7 days posttreatment.
Figures




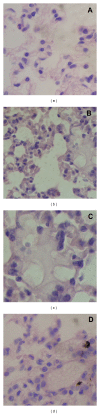

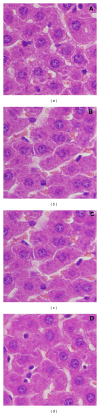

References
-
- Baratli Y, Charles AL, Wolff V, et al. Impact of iron oxide nanoparticles on brain, heart, lung, liver and kidneys mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes activities and coupling. Toxicology in Vitro. 2013;27(8):2142–2148. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira AJ, Cemlyn-Jones J, Robalo Cordeiro C. Nanoparticles, nanotechnology and pulmonary nanotoxicology. Revista Portuguesa de Pneumologia. 2012;19(1):28–37. - PubMed
-
- Mahmoudi M, Sant S, Wang B, Laurent S, Sen T. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2011;63(1-2):24–46. - PubMed
-
- Tari A, Chantrell RW, Charles SW, Popplewell J. The magnetic properties and stability of a ferrofluid containing Fe3O4 particles. Physica B&C. 1979;97(1):57–64.
-
- Poizot P, Laruelle S, Grugeon S, Dupont L, Tarascon J-M. Nano-sized transition-metal oxides as negative-electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Nature. 2000;407(6803):496–499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

