Identification of novel small RNAs and characterization of the 6S RNA of Coxiella burnetii
- PMID: 24949863
- PMCID: PMC4064990
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100147
Identification of novel small RNAs and characterization of the 6S RNA of Coxiella burnetii
Abstract
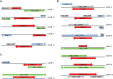
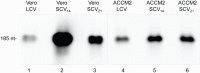
Coxiella burnetii, an obligate intracellular bacterial pathogen that causes Q fever, undergoes a biphasic developmental cycle that alternates between a metabolically-active large cell variant (LCV) and a dormant small cell variant (SCV). As such, the bacterium undoubtedly employs complex modes of regulating its lifecycle, metabolism and pathogenesis. Small RNAs (sRNAs) have been shown to play important regulatory roles in controlling metabolism and virulence in several pathogenic bacteria. We hypothesize that sRNAs are involved in regulating growth and development of C. burnetii and its infection of host cells. To address the hypothesis and identify potential sRNAs, we subjected total RNA isolated from Coxiella cultured axenically and in Vero host cells to deep-sequencing. Using this approach, we identified fifteen novel C. burnetii sRNAs (CbSRs). Fourteen CbSRs were validated by Northern blotting. Most CbSRs showed differential expression, with increased levels in LCVs. Eight CbSRs were upregulated (≥2-fold) during intracellular growth as compared to growth in axenic medium. Along with the fifteen sRNAs, we also identified three sRNAs that have been previously described from other bacteria, including RNase P RNA, tmRNA and 6S RNA. The 6S regulatory sRNA of C. burnetii was found to accumulate over log phase-growth with a maximum level attained in the SCV stage. The 6S RNA-encoding gene (ssrS) was mapped to the 5' UTR of ygfA; a highly conserved linkage in eubacteria. The predicted secondary structure of the 6S RNA possesses three highly conserved domains found in 6S RNAs of other eubacteria. We also demonstrate that Coxiella's 6S RNA interacts with RNA polymerase (RNAP) in a specific manner. Finally, transcript levels of 6S RNA were found to be at much higher levels when Coxiella was grown in host cells relative to axenic culture, indicating a potential role in regulating the bacterium's intracellular stress response by interacting with RNAP during transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
A CsrA-Binding, trans-Acting sRNA of Coxiella burnetii Is Necessary for Optimal Intracellular Growth and Vacuole Formation during Early Infection of Host Cells.J Bacteriol. 2019 Oct 21;201(22):e00524-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00524-19. Print 2019 Nov 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31451541 Free PMC article.
-
Coxiella burnetii RpoS Regulates Genes Involved in Morphological Differentiation and Intracellular Growth.J Bacteriol. 2019 Mar 26;201(8):e00009-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00009-19. Print 2019 Apr 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30745369 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel MITEs (miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements) in Coxiella burnetii: implications for protein and small RNA evolution.BMC Genomics. 2018 Apr 11;19(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4608-y. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29642859 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental biology of Coxiella burnetii.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;984:231-48. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4315-1_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22711635 Review.
-
Small Noncoding 6S RNAs of Bacteria.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2015 Nov;80(11):1429-46. doi: 10.1134/S0006297915110048. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2015. PMID: 26615434 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative transcriptomic analysis of Rickettsia conorii during in vitro infection of human and tick host cells.BMC Genomics. 2020 Sep 25;21(1):665. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07077-w. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32977742 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism and physiology of pathogenic bacterial obligate intracellular parasites.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Mar 22;14:1284701. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1284701. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38585652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Intervening Sequence of Coxiella burnetii: Characterization and Evolution.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Aug 19;6:83. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00083. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27595093 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Novel sRNAs in Streptococcus mutans.J Bacteriol. 2022 Apr 19;204(4):e0057721. doi: 10.1128/jb.00577-21. Epub 2022 Mar 14. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 35285723 Free PMC article.
-
A Small Non-Coding RNA Mediates Transcript Stability and Expression of Cytochrome bd Ubiquinol Oxidase Subunit I in Rickettsia conorii.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 16;24(4):4008. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044008. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835430 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

