CETP inhibitors downregulate hepatic LDL receptor and PCSK9 expression in vitro and in vivo through a SREBP2 dependent mechanism
- PMID: 24950000
- PMCID: PMC4539152
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.05.931
CETP inhibitors downregulate hepatic LDL receptor and PCSK9 expression in vitro and in vivo through a SREBP2 dependent mechanism
Abstract
Background: CETP inhibitors block the transfer of cholesteryl ester from HDL-C to VLDL-C and LDL-C, thereby raising HDL-C and lowering LDL-C. In this study, we explored the effect of CETP inhibitors on hepatic LDL receptor (LDLR) and PCSK9 expression and further elucidated the underlying regulatory mechanism.
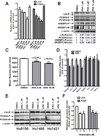
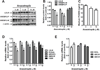
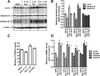
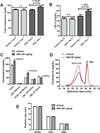
Results: We first examined the effect of anacetrapib (ANA) and dalcetrapib (DAL) on LDLR and PCSK9 expression in hepatic cells in vitro. ANA exhibited a dose-dependent inhibition on both LDLR and PCSK9 expression in CETP-positive HepG2 cells and human primary hepatocytes as well as CETP-negative mouse primary hepatocytes (MPH). Moreover, the induction of LDLR protein expression by rosuvastatin in MPH was blunted by cotreatment with ANA. In both HepG2 and MPH ANA treatment reduced the amount of mature form of SREBP2 (SREBP2-M). In vivo, oral administration of ANA to dyslipidemic C57BL/6J mice at a daily dose of 50 mg/kg for 1 week elevated serum total cholesterol by approximately 24.5% (p < 0.05%) and VLDL-C by 70% (p < 0.05%) with concomitant reductions of serum PCSK9 and liver LDLR/SREBP2-M protein. Finally, we examined the in vitro effect of two other strong CETP inhibitors evacetrapib and torcetrapib on LDLR/PCSK9 expression and observed a similar inhibitory effect as ANA in a concentration range of 1-10 μM.
Conclusion: Our study revealed an unexpected off-target effect of CETP inhibitors that reduce the mature form of SREBP2, leading to attenuated transcription of hepatic LDLR and PCSK9. This negative regulation of SREBP pathway by ANA manifested in mice where CETP activity was absent and affected serum cholesterol metabolism.
Keywords: CETP inhibitors; Hyperlipidemia; LDL receptor; PCSK9; SREBP2.
Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Figures

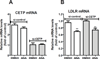



Similar articles
-
Anacetrapib reduces (V)LDL cholesterol by inhibition of CETP activity and reduction of plasma PCSK9.J Lipid Res. 2015 Nov;56(11):2085-93. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M057794. Epub 2015 Sep 4. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 26342106 Free PMC article.
-
An anti-PCSK9 antibody reduces LDL-cholesterol on top of a statin and suppresses hepatocyte SREBP-regulated genes.Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(3):310-27. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.3524. Epub 2012 Feb 9. Int J Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22355267 Free PMC article.
-
New CETP inhibitor K-312 reduces PCSK9 expression: a potential effect on LDL cholesterol metabolism.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Jul 15;309(2):E177-90. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00528.2014. Epub 2015 May 26. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26015437
-
Cholesteryl ester transfer-protein modulator and inhibitors and their potential for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2012;8:323-31. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S25238. Epub 2012 May 15. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2012. PMID: 22661899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On- and off-target pharmacology of torcetrapib: current understanding and implications for the structure activity relationships (SAR), discovery and development of cholesteryl ester-transfer protein (CETP) inhibitors.Drugs. 2012 Mar 5;72(4):491-507. doi: 10.2165/11599310-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22356288 Review.
Cited by
-
Update on dyslipidemia in hypothyroidism: the mechanism of dyslipidemia in hypothyroidism.Endocr Connect. 2022 Feb 7;11(2):e210002. doi: 10.1530/EC-21-0002. Endocr Connect. 2022. PMID: 35015703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A small-molecule inhibitor of PCSK9 transcription ameliorates atherosclerosis through the modulation of FoxO1/3 and HNF1α.EBioMedicine. 2020 Feb;52:102650. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102650. Epub 2020 Feb 12. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32058941 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Metabolism in Pregnancy Women with Hypothyroidism and Potential Influence on Pregnancy Outcome.J Lipids. 2024 Jul 9;2024:5589492. doi: 10.1155/2024/5589492. eCollection 2024. J Lipids. 2024. PMID: 39015803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pinolenic Acid Downregulates Lipid Anabolic Pathway in HepG2 Cells.Lipids. 2016 Jul;51(7):847-55. doi: 10.1007/s11745-016-4149-6. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Lipids. 2016. PMID: 27084371
-
Regulation of lipid metabolism by obeticholic acid in hyperlipidemic hamsters.J Lipid Res. 2017 Feb;58(2):350-363. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M070888. Epub 2016 Dec 9. J Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 27940481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CN, Brewer HB, Jr, Clark LT, Hunninghake DB, Pasternak RC, Smith SC, Jr, Stone NJ. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:720–732. - PubMed
-
- Spady DK. Hepatic clearance of plasma low density lipoproteins. Semin Liver Dis. 1996;12:373–385. - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Goldstein JL. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986;232:34–47. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990;343:425–430. - PubMed
-
- Grundy SM. Statin trials and goals of cholesterol-lowering therapy. Circulation. 1998;97:1436–1439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

