Biomarkers of coronary artery disease: the promise of the transcriptome
- PMID: 24950674
- PMCID: PMC4231210
- DOI: 10.1007/s11886-014-0513-4
Biomarkers of coronary artery disease: the promise of the transcriptome
Abstract
The last years have witnessed tremendous technical advances in the field of transcriptomics that enable the simultaneous assessment of nearly all transcripts expressed in a tissue at a given time. These advances harbor the potential to gain a better understanding of the complex biological systems and for the identification and development of novel biomarkers. This article will review the current knowledge of transcriptomics biomarkers in the cardiovascular field and will provide an overview about the promises and challenges of the transcriptomics approach for biomarker identification.
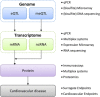
Figures

References
-
- Shanthi Mendis PP, Bo Norrving. World Health Organization, World Heart Federation, World Stroke Organization. Global atlas on cardiovascular disease prevention and control: policies, strategies, and interventions.2011. 164 p.
-
- Perk J, De Backer G, Gohlke H, Graham I, Reiner Z, Verschuren WM, et al. [European Guidelines on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (version 2012). The Fifth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and other societies on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (constituted by representatives of nine societies and by invited experts)]. Giornale italiano di cardiologia. 2013 May;14(5):328-92. Linee guida europee sulla prevenzione delle malattie cardiovascolari nella pratica clinica (versione 2012). Quinta Task Force congiunta della Societa Europea di cardiologia e di altre societa sulla prevenzione delle malattie cardiovascolari nella pratica clinica (costituita da rappresentanti di nove societa e da esperti invitati). - PubMed
-
- Goff DC, Jr., Lloyd-Jones DM, Bennett G, Coady S, D'Agostino RB, Sr., Gibbons R, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2013 Nov 12. - PubMed
-
- Crick FH. On protein synthesis. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1958;12:138–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

