MicroRNA-377 inhibited proliferation and invasion of human glioblastoma cells by directly targeting specificity protein 1
- PMID: 24951112
- PMCID: PMC4201073
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nou111
MicroRNA-377 inhibited proliferation and invasion of human glioblastoma cells by directly targeting specificity protein 1
Abstract
Background: Increasing evidence has indicated that microRNAs (miRNAs) are strongly implicated in the initiation and progression of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). Here, we identified a novel tumor suppressive miRNA, miR-377, and investigated its role and therapeutic effect for GBM.
Methods: MiRNA global screening was performed on GBM patient samples and adjacent nontumor brain tissues. The expression of miR-377 was detected by real-time reverse-transcription PCR. The effects of miR-377 on GBM cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, invasion, and orthotopic tumorigenicity were investigated The therapeutic effect of miR-377 mimic was explored in a subcutaneous GBM model. Western blot and luciferase reporter assay were used to identify the direct and functional target of miR-377.
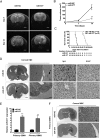
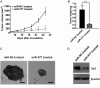
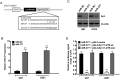
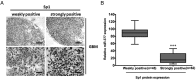
Results: MiR-377 was markedly downregulated in human GBM tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of miR-377 dramatically inhibited cell growth both in culture and in orthotopic xenograft tumor models, blocked G1/S transition, and suppressed cell invasion in GBM cells. Importantly, introduction of miR-377 could strongly inhibit tumor growth in a subcutaneous GBM model. Subsequent investigation revealed that specificity protein 1 (Sp1) was a direct and functional target of miR-377 in GBM cells. Silencing of Sp1 recapitulated the antiproliferative and anti-invasive effects of miR-377, whereas restoring the Sp1 expression antagonized the tumor-suppressive function of miR-377. Finally, analysis of miR-377 and Sp1 levels in human GBM tissues revealed that miR-377 is inversely correlated with Sp1 expression.
Conclusion: These findings reveal that miR-377/Sp1 signaling that may be required for GBM development and may consequently serve as a therapeutic target for the treatment of GBM.
Keywords: Sp1; glioblastoma multiforme; invasion; miR-377; proliferation.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MiR-1271 regulates glioblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by directly targeting the CAMKK2 gene.Neurosci Lett. 2020 Oct 15;737:135289. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135289. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Neurosci Lett. 2020. PMID: 32791096
-
MicroRNA-29a inhibits glioblastoma stem cells and tumor growth by regulating the PDGF pathway.J Neurooncol. 2019 Oct;145(1):23-34. doi: 10.1007/s11060-019-03275-z. Epub 2019 Sep 3. J Neurooncol. 2019. PMID: 31482267 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA‑376a inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in glioblastoma multiforme by directly targeting specificity protein 1.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Jan;17(1):1583-1590. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8089. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29257212 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in human glioblastoma: from bench to beside.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2015 Jan 1;20(1):105-18. doi: 10.2741/4300. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2015. PMID: 25553442 Review.
-
Natural flavonoids alleviate glioblastoma multiforme by regulating long non-coding RNA.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 May;161:114477. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114477. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36931030 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis by Micro-RNAs.J Clin Med. 2019 Nov 20;8(12):2030. doi: 10.3390/jcm8122030. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31757094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-365 suppressed cell proliferation and migration via targeting PAX6 in glioblastoma.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Jan 15;11(1):361-369. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 30787993 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA POU6F2-AS2 promotes cell proliferation and drug resistance in colon cancer by regulating miR-377/BRD4.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Apr;24(7):4136-4149. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15070. Epub 2020 Feb 26. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32100443 Free PMC article.
-
GLUT1 as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Glioblastoma.Brain Sci. 2025 May 28;15(6):585. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15060585. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40563757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ceRNA network of lncRNA MIR210HG/miR-377-3p/LMX1A in malignant proliferation of glioma cells.Genes Genomics. 2022 Dec;44(12):1445-1455. doi: 10.1007/s13258-022-01312-2. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Genes Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36197580
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987–996. - PubMed
-
- He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5(7):522–531. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(11):857–866. - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435(7043):834–838. - PubMed
-
- Shenouda SK, Alahari SK. MicroRNA function in cancer: oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009;28(3–4):369–378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

