NS19504: a novel BK channel activator with relaxing effect on bladder smooth muscle spontaneous phasic contractions
- PMID: 24951278
- PMCID: PMC4152884
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.113.212662
NS19504: a novel BK channel activator with relaxing effect on bladder smooth muscle spontaneous phasic contractions
Abstract
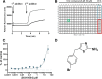
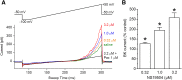
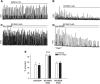
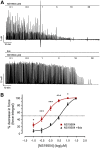
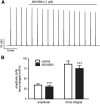
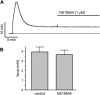
Large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels (BK, KCa1.1, MaxiK) are important regulators of urinary bladder function and may be an attractive therapeutic target in bladder disorders. In this study, we established a high-throughput fluorometric imaging plate reader-based screening assay for BK channel activators and identified a small-molecule positive modulator, NS19504 (5-[(4-bromophenyl)methyl]-1,3-thiazol-2-amine), which activated the BK channel with an EC50 value of 11.0 ± 1.4 µM. Hit validation was performed using high-throughput electrophysiology (QPatch), and further characterization was achieved in manual whole-cell and inside-out patch-clamp studies in human embryonic kidney 293 cells expressing hBK channels: NS19504 caused distinct activation from a concentration of 0.3 and 10 µM NS19504 left-shifted the voltage activation curve by 60 mV. Furthermore, whole-cell recording showed that NS19504 activated BK channels in native smooth muscle cells from guinea pig urinary bladder. In guinea pig urinary bladder strips, NS19504 (1 µM) reduced spontaneous phasic contractions, an effect that was significantly inhibited by the specific BK channel blocker iberiotoxin. In contrast, NS19504 (1 µM) only modestly inhibited nerve-evoked contractions and had no effect on contractions induced by a high K(+) concentration consistent with a K(+) channel-mediated action. Collectively, these results show that NS19504 is a positive modulator of BK channels and provide support for the role of BK channels in urinary bladder function. The pharmacologic profile of NS19504 indicates that this compound may have the potential to reduce nonvoiding contractions associated with spontaneous bladder overactivity while having a minimal effect on normal voiding.
Copyright © 2014 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ethanol-mediated relaxation of guinea pig urinary bladder smooth muscle: involvement of BK and L-type Ca2+ channels.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 Jan 1;306(1):C45-58. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00047.2013. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24153429 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 excitatory effects on guinea pig urinary bladder smooth muscle: a novel regulatory mechanism mediated by large-conductance voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ channels.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Sep 5;738:179-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.05.042. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24886877 Free PMC article.
-
BK channel activation by NS11021 decreases excitability and contractility of urinary bladder smooth muscle.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):R378-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00458.2009. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19923353 Free PMC article.
-
Central role of the BK channel in urinary bladder smooth muscle physiology and pathophysiology.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014 Sep 15;307(6):R571-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00142.2014. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24990859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Big-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels in physiological and pathophysiological urinary bladder smooth muscle cells.Channels (Austin). 2016 Sep 2;10(5):355-364. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2016.1180488. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Channels (Austin). 2016. PMID: 27101440 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of the novel BK (KCa 1.1) channel opener GoSlo-SR-5-130 are dependent on the presence of BKβ subunits.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 May;172(10):2544-56. doi: 10.1111/bph.13085. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25598230 Free PMC article.
-
A computational model of large conductance voltage and calcium activated potassium channels: implications for calcium dynamics and electrophysiology in detrusor smooth muscle cells.J Comput Neurosci. 2019 Jun;46(3):233-256. doi: 10.1007/s10827-019-00713-9. Epub 2019 Apr 25. J Comput Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31025235
-
The Functional Availability of Arterial Kv7 Channels Is Suppressed Considerably by Large-Conductance Calcium-Activated Potassium Channels in 2- to 3-Month Old but Not in 10- to 15-Day Old Rats.Front Physiol. 2020 Dec 15;11:597395. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.597395. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33384611 Free PMC article.
-
Novel cell-free high-throughput screening method for pharmacological tools targeting K+ channels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 May 17;113(20):5748-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1602815113. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27091997 Free PMC article.
-
BK Channel in the Physiology and in the Cancer of Pancreatic Duct: Impact and Reliability of BK Openers.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 24;13:906608. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.906608. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35685628 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahring PK, Strøbaek D, Christophersen P, Olesen SP, Johansen TE. (1997) Stable expression of the human large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel alpha- and beta-subunits in HEK293 cells. FEBS Lett 415:67–70 - PubMed
-
- Andersson KE. (2010) Detrusor myocyte activity and afferent signaling. Neurourol Urodyn 29:97–106 - PubMed
-
- Bentzen BH, Nardi A, Calloe K, Madsen LS, Olesen SP, Grunnet M. (2007) The small molecule NS11021 is a potent and specific activator of Ca2+-activated big-conductance K+ channels. Mol Pharmacol 72:1033–1044 - PubMed
-
- Bentzen BH, Osadchii O, Jespersen T, Hansen RS, Olesen SP, Grunnet M. (2009) Activation of big conductance Ca(2+)-activated K (+) channels (BK) protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Pflugers Arch 457:979–988 - PubMed
-
- Brading AF. (1997) A myogenic basis for the overactive bladder. Urology 50:57–67 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

