Rap2B promotes migration and invasion of human suprarenal epithelioma
- PMID: 24951956
- PMCID: PMC4844085
- DOI: 10.1007/s13277-014-2174-8
Rap2B promotes migration and invasion of human suprarenal epithelioma
Abstract
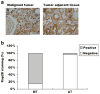
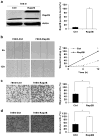
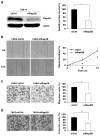
The aim of our study was to elucidate the role of Rap2B in the development of human suprarenal epithelioma and to investigate the effect of Rap2B on suprarenal epithelioma cells migration and invasion. We use tissue microarray and immunohistochemistry to evaluate Rap2B staining in 75 suprarenal epithelioma tissues and 75 tumor-adjacent normal renal tissues. And the expression of Rap2B protein in human suprarenal epithelioma cells and tissues was detected by western blot simultaneously. The role of Rap2B in suprarenal epithelioma cells migration and invasion was detected by using wound healing assay, cell migration assay, and matrigel invasion assay. After that, we performed western blot analysis and gelatin zymography to detect MMP-2 protein expression and enzyme activity. Our research showed that Rap2B expression was increased in tumor tissues compared with tumor-adjacent normal renal tissues. But no correlation was found between Rap2B expression and clinicopathological parameters. In addition, we found that Rap2B promoted the cell migration and invasion abilities, and Rap2B increased MMP-2 expression and enzyme activity in suprarenal epithelioma cells. Our data indicated that Rap2B expression is significantly increased in human suprarenal epithelioma and Rap2B can promote the cell migration and invasion abilities, which may provide a new target for the treatment of suprarenal epithelioma.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
None
Figures
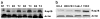

Similar articles
-
Rap2B promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of human breast cancer through calcium-related ERK1/2 signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 23;5:12363. doi: 10.1038/srep12363. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26201295 Free PMC article.
-
Rap2B promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in prostate cancer.Med Oncol. 2016 Jun;33(6):58. doi: 10.1007/s12032-016-0771-7. Epub 2016 May 6. Med Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27154636
-
Rap2B promotes cell adhesion, proliferation, migration and invasion of human glioma.J Neurooncol. 2019 Jun;143(2):221-229. doi: 10.1007/s11060-019-03163-6. Epub 2019 Apr 17. J Neurooncol. 2019. PMID: 30997639
-
Rap2b promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer cells.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2016 Oct;36(5):459-64. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2015.1122044. Epub 2015 Dec 16. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2016. PMID: 26671640
-
Rap2B GTPase: structure, functions, and regulation.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):7085-93. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5033-y. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27012552 Review.
Cited by
-
Rap2B promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of human breast cancer through calcium-related ERK1/2 signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 23;5:12363. doi: 10.1038/srep12363. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26201295 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of Rap2B, a Ras Superfamily Protein, Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Cervical Cancer Cells via Regulating the ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway.Oncol Res. 2018 Jan 19;26(1):123-130. doi: 10.3727/096504017X14912172235777. Epub 2017 Apr 3. Oncol Res. 2018. PMID: 28390112 Free PMC article.
-
p53 target gene Rap2B regulates the cytoskeleton and inhibits cell spreading.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct;141(10):1791-8. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-1948-8. Epub 2015 Mar 12. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25762091 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, functional regulation and signaling properties of Rap2B.Oncol Lett. 2016 Apr;11(4):2339-2346. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4261. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27073477 Free PMC article.
-
Rap2B promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in prostate cancer.Med Oncol. 2016 Jun;33(6):58. doi: 10.1007/s12032-016-0771-7. Epub 2016 May 6. Med Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27154636
References
-
- Kausch I, Jiang H, Ewerdwalbesloh N, Doehn C, Kruger S, Sczakiel G, et al. Inhibition of Ki-67 in a renal cell carcinoma severe combined immunodeficiency disease mouse model is associated with induction of apoptosis and tumour growth inhibition. BJU Int. 2005;95(3):416–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05312.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Janzen NK, Kim HL, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS. Surveillance after radical or partial nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma and management of recurrent disease. Urol Clin N Am. 2003;30(4):843–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

