Isolation of biologically-active exosomes from human plasma
- PMID: 24952243
- PMCID: PMC4260336
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2014.06.007
Isolation of biologically-active exosomes from human plasma
Abstract
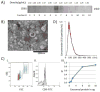
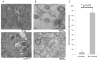
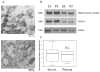
Effects of exosomes present in human plasma on immune cells have not been examined in detail. Immunological studies with plasma-derived exosomes require their isolation by procedures involving ultracentrifugation. These procedures were largely developed using supernatants of cultured cells. To test biologic activities of plasma-derived exosomes, methods are necessary that ensure adequate recovery of exosome fractions free of contaminating larger vesicles, cell fragments and protein/nucleic acid aggregates. Here, an optimized method for exosome isolation from human plasma/serum specimens of normal controls (NC) or cancer patients and its advantages and pitfalls are described. To remove undesirable plasma-contaminating components, ultrafiltration of differentially-centrifuged plasma/serum followed by size-exclusion chromatography prior to ultracentrifugation facilitated the removal of contaminants. Plasma or serum was equally acceptable as a source of exosomes based on the recovered protein levels (in μg protein/mL plasma) and TEM image quality. Centrifugation on sucrose density gradients led to large exosome losses. Fresh plasma was the best source of morphologically-intact exosomes, while the use of frozen/thawed plasma decreased exosome purity but not their biologic activity. Treatments of frozen plasma with DNAse, RNAse or hyaluronidase did not improve exosome purity and are not recommended. Cancer patients' plasma consistently yielded more isolated exosomes than did NCs' plasma. Cancer patients' exosomes also mediated higher immune suppression as evidenced by decreased CD69 expression on responder CD4+ T effector cells. Thus, the described procedure yields biologically-active, morphologically-intact exosomes that have reasonably good purity without large protein losses and can be used for immunological, biomarker and other studies.
Keywords: Exosome characteristics; Exosome isolation; Human plasma; Immunological studies; Size-exclusion chromatography.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Bianco NR, Kim SH, Morelli AE, Robbins PD. Modulation of the immune response using dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2007;380:443–55. - PubMed
-
- Clayton A, Court J, Navabi H, Adams M, Mason MD, Hobot JA, Newman GR, Jasani B. Analysis of antigen presenting cell derived exosomes, based on immuno-magnetic isolation and flow cytometry. Journal of Immunological Methods. 2001;247:163–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

