The Src homology-2 protein Shb modulates focal adhesion kinase signaling in a BCR-ABL myeloproliferative disorder causing accelerated progression of disease
- PMID: 24952416
- PMCID: PMC4074852
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8722-7-45
The Src homology-2 protein Shb modulates focal adhesion kinase signaling in a BCR-ABL myeloproliferative disorder causing accelerated progression of disease
Abstract
Background: The Src homology-2 domain protein B (Shb) is an adapter protein operating downstream of several tyrosine kinase receptors and consequently Shb regulates various cellular responses. Absence of Shb was recently shown to reduce hematopoietic stem cell proliferation through activation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and thus we sought to investigate Shb's role in the progression of leukemia.
Methods: Wild type and Shb knockout bone marrow cells were transformed with a retroviral BCR-ABL construct and subsequently transplanted to wild type or Shb knockout recipients. Disease latency, bone marrow and peripheral blood cell characteristics, cytokine expression, signaling characteristics and colony formation were determined by flow cytometry, qPCR, western blotting and methylcellulose colony forming assays.
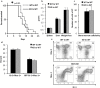
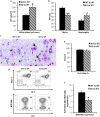
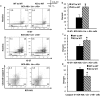
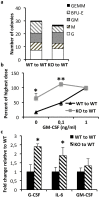
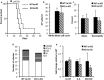
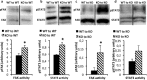
Results: It was observed that Shb knockout BCR-ABL-transformed bone marrow cells produced a disease with death occurring at earlier time points compared with corresponding wild type controls due to elevated proliferation of transformed bone marrow cells. Moreover, significantly elevated interleukin-6 and granulocyte colony-stimulation factor mRNA levels were observed in Shb knockout c-Kit + leukemic bone marrow cells providing a plausible explanation for the concurrent peripheral blood neutrophilia. Shb knockout leukemic bone marrow cells also showed increased ability to form colonies in methylcellulose devoid of cytokines that was dependent on the concomitantly observed increased activity of FAK. Transplanting BCR-ABL-transformed Shb knockout bone marrow cells to Shb knockout recipients revealed decreased disease latency without neutrophilia, thus implicating the importance of niche-derived cues for the increase of blood granulocytes.
Conclusions: Absence of Shb accelerates disease progression by exerting dual roles in BCR-ABL-induced leukemia: increased cell expansion due to elevated FAK activity and neutrophilia in peripheral blood, the latter dependent on the genetic background of the leukemic niche.
Figures

References
-
- Thomas EK, Cancelas JA, Chae HD, Cox AD, Keller PJ, Perrotti D, Neviani P, Druker BJ, Setchell KD, Zheng Y, Harris CE, Williams DA. Rac guanosine triphosphatases represent integrating molecular therapeutic targets for BCR-ABL-induced myeloproliferative disease. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:467–478. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2007.10.015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

