In vivo RNA interference models of inducible and reversible Sirt1 knockdown in kidney cells
- PMID: 24952428
- PMCID: PMC4076473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.03.016
In vivo RNA interference models of inducible and reversible Sirt1 knockdown in kidney cells
Abstract
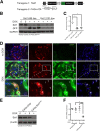
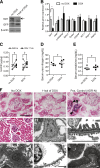
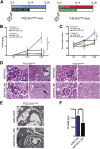
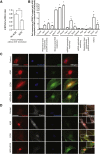
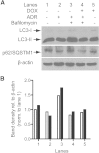
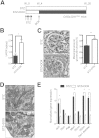
The silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 1 gene (Sirt1) encodes an NAD-dependent deacetylase that modifies the activity of well-known transcriptional regulators affected in kidney diseases. Sirt1 is expressed in the kidney podocyte, but its function in the podocyte is not clear. Genetically engineered mice with inducible and reversible Sirt1 knockdown in widespread, podocyte-specific, or tubular-specific patterns were generated. We found that mice with 80% knockdown of renal Sirt1 expression have normal glomerular function under the basal condition. When challenged with doxorubicin (Adriamycin), these mice develop marked albuminuria, glomerulosclerosis, mitochondrial injury, and impaired autophagy of damaged mitochondria. Reversal of Sirt1 knockdown during the early phase of Adriamycin-induced nephropathy prevented the progression of glomerular injury and reduced the accumulation of dysmorphic mitochondria in podocytes but did not reverse the progression of albuminuria and glomerulosclerosis. Sirt1 knockdown mice with diabetes mellitus, which is known to cause mitochondrial dysfunction in the kidney, developed more albuminuria and mitochondrial dysfunction compared with diabetic mice without Sirt1 knockdown. In conclusion, these results demonstrate that our RNA interference-mediated Sirt1 knockdown models are valid and versatile tools for characterizing the function of Sirt1 in the kidney; Sirt1 plays a role in homeostatic maintenance of podocytes under the condition of mitochondrial stress/injury.
Copyright © 2014 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
METTL14 aggravates podocyte injury and glomerulopathy progression through N6-methyladenosine-dependent downregulating of Sirt1.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Sep 27;12(10):881. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04156-y. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34580283 Free PMC article.
-
Increased podocyte Sirtuin-1 function attenuates diabetic kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2018 Jun;93(6):1330-1343. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.12.008. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Kidney Int. 2018. PMID: 29477240 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α ameliorates mitochondrial dysfunction and protects podocytes from aldosterone-induced injury.Kidney Int. 2012 Oct;82(7):771-89. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.188. Epub 2012 May 30. Kidney Int. 2012. PMID: 22648295
-
Communication from Tubular Epithelial Cells to Podocytes through Sirt1 and Nicotinic Acid Metabolism.Curr Hypertens Rev. 2016;12(2):95-104. doi: 10.2174/1573402112666160302102217. Curr Hypertens Rev. 2016. PMID: 26931474 Review.
-
Ability of NAD and Sirt1 to epigenetically suppress albuminuria.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2024 Jul;28(7):599-607. doi: 10.1007/s10157-024-02502-w. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38587753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sirtuin 1 in Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Sirtuin 1.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 20;13:917773. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.917773. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35795148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL14 aggravates podocyte injury and glomerulopathy progression through N6-methyladenosine-dependent downregulating of Sirt1.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Sep 27;12(10):881. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04156-y. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34580283 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and chronic kidney disease: Insights on lipid metabolism of tubular epithelial cell and macrophages in tubulointerstitial fibrosis.Front Physiol. 2023 Mar 29;14:1145233. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1145233. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37064892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Puerarin attenuates diabetic kidney injury through the suppression of NOX4 expression in podocytes.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 6;7(1):14603. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14906-8. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29097815 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin Protects against Podocyte Injury in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Dec 10;13(12):452. doi: 10.3390/ph13120452. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33321755 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Salminen A., Kaarniranta K. SIRT1: regulation of longevity via autophagy. Cell Signal. 2009;21:1356–1360. - PubMed
-
- Rodgers J.T., Lerin C., Haas W., Gygi S.P., Spiegelman B.M., Puigserver P. Nutrient control of glucose homeostasis through a complex of PGC-1alpha and SIRT1. Nature. 2005;434:113–118. - PubMed
-
- Nemoto S., Fergusson M.M., Finkel T. SIRT1 functionally interacts with the metabolic regulator and transcriptional coactivator PGC-1{alpha} J Biol Chem. 2005;280:16456–16460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

