The kinesin-4 protein Kif7 regulates mammalian Hedgehog signalling by organizing the cilium tip compartment
- PMID: 24952464
- PMCID: PMC4085576
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988
The kinesin-4 protein Kif7 regulates mammalian Hedgehog signalling by organizing the cilium tip compartment
Abstract
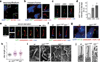
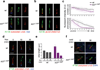
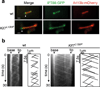
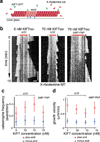
Mammalian Hedgehog (Hh) signal transduction requires a primary cilium, a microtubule-based organelle, and the Gli-Sufu complexes that mediate Hh signalling, which are enriched at cilia tips. Kif7, a kinesin-4 family protein, is a conserved regulator of the Hh signalling pathway and a human ciliopathy protein. Here we show that Kif7 localizes to the cilium tip, the site of microtubule plus ends, where it limits cilium length and controls cilium structure. Purified recombinant Kif7 binds the plus ends of growing microtubules in vitro, where it reduces the rate of microtubule growth and increases the frequency of microtubule catastrophe. Kif7 is not required for normal intraflagellar transport or for trafficking of Hh pathway proteins into cilia. Instead, a central function of Kif7 in the mammalian Hh pathway is to control cilium architecture and to create a single cilium tip compartment, where Gli-Sufu activity can be correctly regulated.
Figures

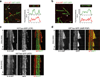
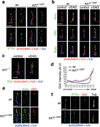
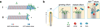
Comment in
-
Kif7 keeps cilia tips in shape.Nat Cell Biol. 2014 Jul;16(7):623-5. doi: 10.1038/ncb2997. Nat Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24981634
-
Organelle dynamics. KIF7 organizes cilia.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Aug;15(8):498-9. doi: 10.1038/nrm3839. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25005343
-
Location, location, and location: compartmentalization of Hedgehog signaling at primary cilia.EMBO J. 2014 Sep 1;33(17):1852-4. doi: 10.15252/embj.201489294. Epub 2014 Jul 17. EMBO J. 2014. PMID: 25037564 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

