HGF/c-Met axis drives cancer aggressiveness in the neo-adjuvant setting of ovarian cancer
- PMID: 24952592
- PMCID: PMC4148105
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2049
HGF/c-Met axis drives cancer aggressiveness in the neo-adjuvant setting of ovarian cancer
Abstract
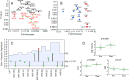
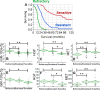
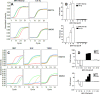
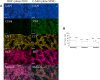
Ovarian cancer is the most lethal gynecologic malignancy. Recently, NACT (Neo Adjuvant Chemotherapy) has been tested as alternative approach for the management of ovarian cancer patients. A biological predictor helpful in selecting patients for NACT would be desirable. This study was aimed at identifying actionable mechanisms of resistance to NACT. Expression of a panel of microRNAs was screened in a discovery set of 85 patients. Analysis of the potential targets was conducted in the same RNAs by calculating significant correlations between microRNAs and genes. Quantitative fluorescent immunohistochemistry was employed in a validation set of 109 patients. MiR-193a-5p was significantly overexpressed in the NACT setting. Analysis of its potential targets demonstrated that this microRNA is also significantly correlated with HGF and MET genes. Analysis of protein expression in samples taken before and after NACT demonstrated that both HGF and c-Met are increased after NACT. Patients who relapse shortly after NACT exhibited the highest relative basal expression of both HGF and c-Met, while the opposite phenomenon was observed in the best responders. Mir-193a-5p, HGF and c-Met expression may help select eligible patients for this modality of treatment. Moreover, inhibitors of this pathway may improve the efficacy of NACT.
Figures
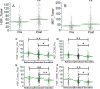
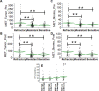
References
-
- Kyrgiou M, Salanti G, Pavlidis N, Paraskevaidis E, Ioannidis JP. Survival benefits with diverse chemotherapy regimens for ovarian cancer: meta-analysis of multiple treatments. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98(22):1655–1663. - PubMed
-
- Vergote I, Trope CG, Amant F, Kristensen GB, Ehlen T, Johnson N, Verheijen RH, van der Burg ME, Lacave AJ, Panici PB, Kenter GG, Casado A, Mendiola C, Coens C, Verleye L, Stuart GC, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy or primary surgery in stage IIIC or IV ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(10):943–953. - PubMed
-
- McLean KA, Shah CA, Thompson SA, Gray HJ, Swensen RE, Goff BA. Ovarian cancer in the elderly: outcomes with neoadjuvant chemotherapy or primary cytoreduction. Gynecol Oncol. 2010;118(1):43–46. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz PE. Contemporary considerations for neoadjuvant chemotherapy in primary ovarian cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2009;11(6):457–465. - PubMed
-
- Chi DS, Musa F, Dao F, Zivanovic O, Sonoda Y, Leitao MM, Levine DA, Gardner GJ, Abu-Rustum NR, Barakat RR. An analysis of patients with bulky advanced stage ovarian, tubal, and peritoneal carcinoma treated with primary debulking surgery (PDS) during an identical time period as the randomized EORTC-NCIC trial of PDS vs neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) Gynecol Oncol. 2012;124(1):10–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

