Noninvasive two-photon microscopy imaging of mouse retina and retinal pigment epithelium through the pupil of the eye
- PMID: 24952647
- PMCID: PMC4087080
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3590
Noninvasive two-photon microscopy imaging of mouse retina and retinal pigment epithelium through the pupil of the eye
Abstract
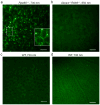
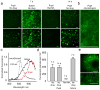
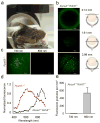
Two-photon excitation microscopy can image retinal molecular processes in vivo. Intrinsically fluorescent retinyl esters in subcellular structures called retinosomes are an integral part of the visual chromophore regeneration pathway. Fluorescent condensation products of all-trans-retinal accumulate in the eye with age and are also associated with age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Here, we report repetitive, dynamic imaging of these compounds in live mice through the pupil of the eye. By leveraging advanced adaptive optics, we developed a data acquisition algorithm that permitted the identification of retinosomes and condensation products in the retinal pigment epithelium by their characteristic localization, spectral properties and absence in genetically modified or drug-treated mice. This imaging approach has the potential to detect early molecular changes in retinoid metabolism that trigger light- and AMD-induced retinal defects and to assess the effectiveness of treatments for these conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Financial Interests: G.P. and Z.D. are employees of Polgenix. K.P. is CSO at Polgenix Inc. K.P. is an inventor of the U.S. Patent No. 7,706,863 and U.S. Patent No. 8,346,345 whose value may be affected by this publication. N.S.A and M.G., report no conflict of interest. The J.J.H and D.R.W. laboratories received support from Polgenix Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Helmchen F, Denk W. Deep tissue two-photon microscopy. Nat Methods. 2005;2:932–940. - PubMed
-
- Boettner EA, Wolter JR. Transmission of the oculer media. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1962;1:776–183.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 EY011373/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY008061/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R24EY021126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY008061/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32DK007319/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R44 AG043645/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R44AG043645/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY009339/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EY007157/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30EY11373/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32EY007157/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY009339/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007319/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 EY021126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

