All-optical electrophysiology in mammalian neurons using engineered microbial rhodopsins
- PMID: 24952910
- PMCID: PMC4117813
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.3000
All-optical electrophysiology in mammalian neurons using engineered microbial rhodopsins
Abstract
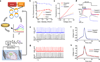
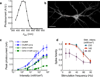
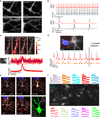
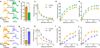
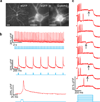
All-optical electrophysiology-spatially resolved simultaneous optical perturbation and measurement of membrane voltage-would open new vistas in neuroscience research. We evolved two archaerhodopsin-based voltage indicators, QuasAr1 and QuasAr2, which show improved brightness and voltage sensitivity, have microsecond response times and produce no photocurrent. We engineered a channelrhodopsin actuator, CheRiff, which shows high light sensitivity and rapid kinetics and is spectrally orthogonal to the QuasArs. A coexpression vector, Optopatch, enabled cross-talk-free genetically targeted all-optical electrophysiology. In cultured rat neurons, we combined Optopatch with patterned optical excitation to probe back-propagating action potentials (APs) in dendritic spines, synaptic transmission, subcellular microsecond-timescale details of AP propagation, and simultaneous firing of many neurons in a network. Optopatch measurements revealed homeostatic tuning of intrinsic excitability in human stem cell-derived neurons. In rat brain slices, Optopatch induced and reported APs and subthreshold events with high signal-to-noise ratios. The Optopatch platform enables high-throughput, spatially resolved electrophysiology without the use of conventional electrodes.
Figures
References
Supplementary References
-
- Zhao H, Giver L, Shao Z, Affholter JA, Arnold FH. Molecular evolution by staggered extension process (StEP) in vitro recombination. Nat. Biotechnol. 1998;16:258–261. - PubMed
-
- Cheng Z, Campbell RE. Assessing the structural stability of designed β-hairpin peptides in the cytoplasm of live cells. ChemBioChem. 2006;7:1147–1150. - PubMed
-
- Lanyi JK. Proton translocation mechanism and energetics in the light-driven pump bacteriorhodopsin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1993;1183:241–261. - PubMed
-
- Lanyi JK. Bacteriorhodopsin. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2004;66:665–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DP2 OD007428/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- R01 DC011291/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 OD002002/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS046579/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS075421/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS067199/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA029639/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 1-R01-EB012498-01/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS039059/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES002109/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC013329/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB012498/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 1-DP2-OD007428/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

