Platelet response to serotonin in patients with stable coronary heart disease
- PMID: 24952926
- PMCID: PMC4130397
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.04.023
Platelet response to serotonin in patients with stable coronary heart disease
Abstract
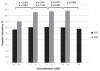
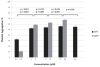
Patients with heart disease and depression have an increased mortality rate. Both behavioral and biologic factors have been proposed as potential etiologic mechanisms. Given that the pathophysiology of depression is considered to involve disruption in brain serotonergic signaling, we investigated platelet response to serotonin stimulation in patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD). We enrolled 92 patients with stable CAD. Platelet response to increasing concentrations of serotonin (5-HT), epinephrine-augmented 5-HT, and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) was measured by optical aggregation and flow cytometry. As concentrations of 5-HT and ADP increased, so did the activation and aggregation of the platelets. However, on addition of the highest concentration of 5-HT (30 μM), a significant decrease in platelet activation (p=0.005) was detected by flow cytometry. This contrasts the increase in platelet activation seen with the addition of the highest concentration of ADP. In conclusion, we found increased platelet activation and aggregation with increased concentrations of ADP; however, when platelets are stimulated with a high concentration of 5-HT (30 μM), there is decreased platelet activation. The data demonstrate unique patterns of platelet activation by 5-HT in patients with stable CAD. The cause of this phenomenon is unclear. Our study sheds light on the in vitro response of platelet function to serotonin in patients with stable CAD, which may further the mechanistic understanding of heart disease and depression.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Maree AO, Fitzgerald DJ. Aspirin and coronary artery disease. Thromb Haemost. 2004;92:1175–1181. - PubMed
-
- Reid GJ, Seidelin PH, Kop WJ, Irvine MJ, Strauss BH, Nolan RP, Lau HK, Yeo EL. Mental-stress-induced platelet activation among patients with coronary artery disease. Psychosom Med. 2009;71:438–445. - PubMed
-
- McCaffery JM, Frasure-Smith N, Dube MP, Theroux P, Rouleau GA, Duan Q, Lesperance F. Common genetic vulnerability to depressive symptoms and coronary artery disease: a review and development of candidate genes related to inflammation and serotonin. Psychosom Med. 2006;68:187–200. - PubMed
-
- Shimbo D, Child J, Davidson K, Geer E, Osende JI, Reddy S, Dronge A, Fuster V, Badimon JJ. Exaggerated serotonin-mediated platelet reactivity as a possible link in depression and acute coronary syndromes. Am J Cardiol. 2002;89:331–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

