Synergic role of nucleophosmin three-helix bundle and a flanking unstructured tail in the interaction with G-quadruplex DNA
- PMID: 24952945
- PMCID: PMC4118085
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.565010
Synergic role of nucleophosmin three-helix bundle and a flanking unstructured tail in the interaction with G-quadruplex DNA
Abstract
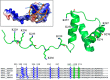
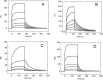
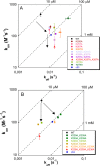
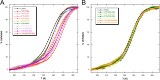
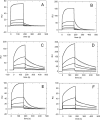
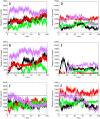
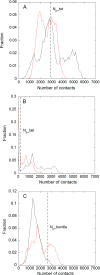
Nucleophosmin (NPM1) is a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein, mainly localized at nucleoli, that plays a number of functions in ribosome biogenesis and export, cell cycle control, and response to stress stimuli. NPM1 is the most frequently mutated gene in acute myeloid leukemia; mutations map to the C-terminal domain of the protein and cause its denaturation and aberrant cytoplasmic translocation. NPM1 C-terminal domain binds G-quadruplex regions at ribosomal DNA and at gene promoters, including the well characterized sequence from the nuclease-hypersensitive element III region of the c-MYC promoter. These activities are lost by the leukemic variant. Here we analyze the NPM1/G-quadruplex interaction, focusing on residues belonging to both the NPM1 terminal three-helix bundle and a lysine-rich unstructured tail, which has been shown to be necessary for high affinity recognition. We performed extended site-directed mutagenesis and measured binding rate constants through surface plasmon resonance analysis. These data, supported by molecular dynamics simulations, suggest that the unstructured tail plays a double role in the reaction mechanism. On the one hand, it facilitates the formation of an encounter complex through long range electrostatic interactions; on the other hand, it directly contacts the G-quadruplex scaffold through multiple and transient electrostatic interactions, significantly enlarging the contact surface.
Keywords: Encounter Complex; Flanking Fuzziness; Intrinsically Disordered Protein; Leukemia; Molecular Dynamics; Protein-DNA Interaction; Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR).
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Kang Y. J., Olson M. O., Jones C., Busch H. (1975) Nucleolar phosphoproteins of normal rat liver and Novikoff hepatoma ascites cells. Cancer Res. 35, 1470–1475 - PubMed
-
- Borer R. A., Lehner C. F., Eppenberger H. M., Nigg E. A. (1989) Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell 56, 379–390 - PubMed
-
- Okuwaki M., Matsumoto K., Tsujimoto M., Nagata K. (2001) Function of nucleophosmin/B23, a nucleolar acidic protein, as a histone chaperone. FEBS Lett. 506, 272–276 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

