Leptin-receptor-expressing mesenchymal stromal cells represent the main source of bone formed by adult bone marrow
- PMID: 24953181
- PMCID: PMC4127103
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.06.008
Leptin-receptor-expressing mesenchymal stromal cells represent the main source of bone formed by adult bone marrow
Abstract
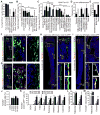
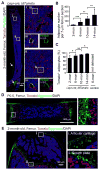
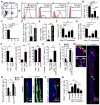
Studies of the identity and physiological function of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) have been hampered by a lack of markers that permit both prospective identification and fate mapping in vivo. We found that Leptin Receptor (LepR) is a marker that highly enriches bone marrow MSCs. Approximately 0.3% of bone marrow cells were LepR(+), 10% of which were CFU-Fs, accounting for 94% of bone marrow CFU-Fs. LepR(+) cells formed bone, cartilage, and adipocytes in culture and upon transplantation in vivo. LepR(+) cells were Scf-GFP(+), Cxcl12-DsRed(high), and Nestin-GFP(low), markers which also highly enriched CFU-Fs, but negative for Nestin-CreER and NG2-CreER, markers which were unlikely to be found in CFU-Fs. Fate-mapping showed that LepR(+) cells arose postnatally and gave rise to most bone and adipocytes formed in adult bone marrow, including bone regenerated after irradiation or fracture. LepR(+) cells were quiescent, but they proliferated after injury. Therefore, LepR(+) cells are the major source of bone and adipocytes in adult bone marrow.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Leptin receptor makes its mark on MSCs.Cell Stem Cell. 2014 Aug 7;15(2):112-4. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.07.001. Cell Stem Cell. 2014. PMID: 25105573
References
-
- Buch T, Heppner FL, Tertilt C, Heinen TJ, Kremer M, Wunderlich FT, Jung S, Waisman A. A Cre-inducible diphtheria toxin receptor mediates cell lineage ablation after toxin administration. Nat Methods. 2005;2:419–426. - PubMed
-
- Chai Y, Jiang X, Ito Y, Bringas P, Jr, Han J, Rowitch DH, Soriano P, McMahon AP, Sucov HM. Fate of the mammalian cranial neural crest during tooth and mandibular morphogenesis. Development. 2000;127:1671–1679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

