Reduction of angiotensin A and alamandine vasoactivity in the rabbit model of atherogenesis: differential effects of alamandine and Ang(1-7)
- PMID: 24953785
- PMCID: PMC4170971
- DOI: 10.1111/iep.12087
Reduction of angiotensin A and alamandine vasoactivity in the rabbit model of atherogenesis: differential effects of alamandine and Ang(1-7)
Abstract
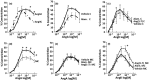
Novel treatments are necessary to reduce the burden of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Alamandine binds to MrgD and is reported to induce vasodilation via stimulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), but its role in atherogenic blood vessels is yet to be determined. To determine the vasoactive role of alamandine and its precursor AngA in diseased aorta, New Zealand White rabbits were fed a diet containing 1% methionine + 0.5% cholesterol + 5% peanut oil for 4 weeks (MC, n = 5) or control (n = 6). In abdominal aorta, alamandine (1 μM) was added 30 min before a dose-response curve to angiotensin II or AngA (1 nM-1 μM), and immunohistochemistry was used to identify MrgD receptors and eNOS. The thoracic aorta, renal, carotid and iliac arteries were mounted in organ baths. Rings were precontracted with phenylephrine, then a bolus dose of alamandine (1 μM) was added 10 min before a dose-response curve to acetylcholine (0.01 μM-10 μM). The MrgD receptor was localized to normal and diseased aorta and colocalized with eNOS. In control but not diseased blood vessels, alamandine enhanced acetylcholine-mediated vasodilation in the thoracic aorta and the iliac artery (P < 0.05) and reduced it in the renal artery (P < 0.05). In control abdominal aorta, AngA evoked less desensitization than AngII (P < 0.05) and alamandine reduced AngA-mediated vasoconstriction (P < 0.05). In MC, AngA constriction was markedly reduced vs. control (P < 0.05). The vasoactivity of alamandine and AngA are reduced in atherogenesis. Its role in the prevention of CVD remains to be validated.
Keywords: alamandine; angiotensin A; atherosclerosis; endothelial dysfunction.
© 2014 The Authors. International Journal of Experimental Pathology © 2014 International Journal of Experimental Pathology.
Figures


References
-
- Freeman EJ, Chisolm GM, Ferrario CM, Tallant EA. Angiotensin-(1-7) inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell growth. Hypertension. 1996;28:104–108. - PubMed
-
- Iusuf D, Henning RH, van Gilst WH, Roks AJ. Angiotensin-(1-7): pharmacological properties and pharmacotherapeutic perspectives. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008;585:303–312. - PubMed
-
- Jankowski V, Vanholder R, van der Giet M, et al. Mass-spectrometric identification of a novel angiotensin peptide in human plasma. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007;27:297–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

