Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for preserving residual kidney function in peritoneal dialysis patients
- PMID: 24953826
- PMCID: PMC8938932
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009120.pub2
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for preserving residual kidney function in peritoneal dialysis patients
Abstract
Background: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEis) and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are widely used in peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients, yet controversy exists about their impact on residual kidney function.
Objectives: This review aimed to evaluate the benefits and harms of ACEis and ARBs for preserving residual kidney function in PD patients.
Search methods: The Cochrane Renal Group's specialised register, Cochrane Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, EMBASE (OvidSP interface), Chinese Biomedical Literature Database (CBM), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) and other resources were searched by applying a prespecified comprehensive search strategy. Date of last search: 01 May 2014.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi-RCTs comparing ACEis or ARBs with placebo, other antihypertensive drugs or each other in PD patients were included.
Data collection and analysis: Screening, selection, data extraction and quality assessments for each retrieved article were carried out by two authors using standardised forms. Authors were contacted when published data were incomplete. Statistical analyses were performed using the random effects model and results expressed as risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Heterogeneity among studies was explored using the Cochran Q statistic and the I² test, subgroup analyses and random effects meta-regression.
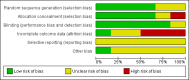
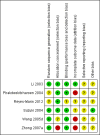
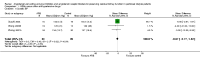
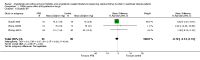
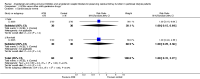
Main results: Six open-label studies (257 patients) were identified. One study compared ACEi with other antihypertensive drugs, three compared ARBs with other antihypertensive drugs, and two studies compared an ARB with an ACEi. Long-term use (≥ 12 months) of an ARB showed significantly benefit of preserving residual kidney function in continuous ambulatory PD (CAPD) patients (MD 1.11 mL/min/1.73 m², 95% CI 0.38 to 1.83), although there was no significant benefit when an ARB were used short-term (≤ six months). One study showed that compared with other antihypertensive drugs, long-term use (12 months) of the ACEi ramipril showed a significant reduction in the decline of residual kidney function in patients on CAPD (MD -0.93 mL/min/1.73m², 95% CI -0.75 to -0.11), and delayed the progression to complete anuria (RR 0.64, 95% CI 0.41 to 0.99). There was no significant difference in serum potassium, urinary protein excretion, Kt/V, weekly creatinine clearance and blood pressure for ARBs versus other antihypertensive drugs. Compared with other antihypertensive drugs, ramipril showed no difference in mortality and cardiovascular events. Compared with an ACEi, ARBs did not show any difference in residual kidney function.The selection bias assessment was low in four studies and unclear in two. Five studies were open-label; however the primary outcome (residual kidney function) was obtained objectively from laboratory tests, and were not likely to be influenced by the lack of blinding. Reporting bias was unclear in all six studies.
Authors' conclusions: Compared with other antihypertensive drugs, long-term use (≥ 12 months) of ACEis or ARBs showed additional benefits of preserving residual kidney function in CAPD patients. There was no significant difference on residual kidney function preservation between ARBs and ACEis. However, limited by the small number of RCTs enrolling small number of participants, there is currently insufficient evidence to support the use of an ACEi or an ARB as first line antihypertensive therapy in PD patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Ling Zhang: none known
Xiaoxi Zeng: none known
Ping Fu: none known
Hong Mei Wu: none known
Figures





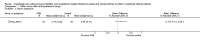







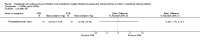


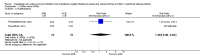
Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009120
Similar articles
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for adults with early (stage 1 to 3) non-diabetic chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Oct 5;(10):CD007751. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007751.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 19;7:CD007751. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007751.pub3. PMID: 21975774 Updated.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for adults with early (stage 1 to 3) non-diabetic chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 19;7(7):CD007751. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007751.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37466151 Free PMC article.
-
Antihypertensive agents for preventing diabetic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD004136. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004136.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235603 Free PMC article.
-
ACE Inhibitor Benefit to Kidney and Cardiovascular Outcomes for Patients with Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3-5: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomised Clinical Trials.Drugs. 2020 Jun;80(8):797-811. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01290-3. Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32333236 Free PMC article.
-
Aldosterone antagonists for preventing the progression of chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;(4):CD007004. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007004.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 27;10:CD007004. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007004.pub4. PMID: 24782282 Updated.
Cited by
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blocker use and cardiovascular outcomes in patients initiating peritoneal dialysis.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017 May 1;32(5):862-869. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfw053. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017. PMID: 27190342 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockade on Residual Kidney Function and Peritoneal Membrane Function in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Network Meta-Analysis.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 20;9(1):19582. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55561-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31862905 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular death, and cardiovascular events among peritoneal dialysis patients: A protocol for systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Apr;99(17):e19767. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019767. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32332616 Free PMC article.
-
Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System Blockades Does Not Protect Residual Renal Function in Patients with Hemodialysis at 1 Year After Dialysis Initiation: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 2;9(1):18103. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54572-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31792268 Free PMC article.
-
Association of blood pressure after peritoneal dialysis initiation with the decline rate of residual kidney function in newly-initiated peritoneal dialysis patients.PLoS One. 2021 Jul 8;16(7):e0254169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254169. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34237104 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
Li 2003 {published data only}
-
- Li PK, Chow K, Wong TY, Leung C, Szeto CC. Effects of an angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitor on residual renal function in patients receiving peritoneal dialysis. A randomized, controlled study. Annals of Internal Medicine 2003;139(2):105‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Li PK, Chow K, Wong TY, Leung C, Szeto CC. Preservation of residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis patients by angiotensin‐converting‐enzyme inhibitor ‐ a prospective study [abstract no: F‐FC004]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2002;13(September, Program & Abstracts):1a. [CENTRAL: CN‐00446373]
Phakdeekitcharoen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Phakdeekitcharoen B, Leelasa‐nguan P. Effects of an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker on potassium in CAPD patients. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2004;44(4):738‐46. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Reyes‐Marin 2012 {published data only}
-
- Reyes‐Marin FA, Calzada C, Ballesteros A, Amato D. Comparative study of enalapril vs. losartan on residual renal function preservation in automated peritoneal dialysis. A randomized controlled study. Revista de Investigacion Clinica 2012;64(4):315‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Suzuki 2004 {published data only}
-
- Suzuki H, Kanno Y, Sugahara S. Effects of an angiotensin II receptor blocker, valsartan, on residual renal function in patients on CAPD. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2004;43(6):1056‐64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wang 2005d {published data only}
-
- Wang J, Xiao MY. Protective effects of valsartan on residual renal function in patients on CAPD. Chinese Journal of Blood Purification 2005;4(11):605‐6.
Zhong 2007a {published data only}
-
- Zhong H, Sha CH, Sui TL, Qiu HY, Liu F, Qin W, et al. Effects of irbesartan on residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis patients. Chinese Journal of Nephrology 2007;23(7):413‐6.
References to studies excluded from this review
Cioni 2010 {published data only}
-
- Cioni A, Sordini C, Cavallini I, Bigazzi R, Vito M, Campese VM. Angiotensin receptor blocker telmisartan improves insulin sensitivity in peritoneal dialysis patients. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2010;30(1):66‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Favazza 1992 {published data only}
-
- Favazza A, Motanaro D, Messa P, Antonucci F, Gropuzzo M, Mioni G. Peritoneal clearances in hypertensive CAPD patients after oral administration of clonidine, enalapril, and nifedipine. Peritoneal Dialysis International 1992;12(3):287‐91. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Huang 2002 {published data only}
-
- Huang YH. Effect of angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors on serum levels of erythropoietin in patients on peritoneal dialysis. Di Yi Junyi Daxue Xuebao 2002;22(1):74‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kolesnyk 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kolesnyk I, Noordzij M, Dekker FW, Boeschoten EW, Krediet RT. Treatment with angiotensin II inhibitors and residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis patients. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2011;31(1):53‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nakamoto 2004 {published data only}
-
- Nakamoto H, Kanno Y, Okada H, Suzuki H. Erythropoietin resistance in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis 2004;20:111‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
PERFECT Study 1997 {published data only}
-
- Collins JF, Robson R, MacMahon S, Bailey RR, PERFECT Study Group. Safety and efficacy of enalapril and simvastatin in dialysis patients [abstract]. 6th Asian Pacific Congress of Nephrology; 1995 Dec 5‐9; Hong Kong. 1995:144. [CENTRAL: CN‐00460572]
-
- Robson R, Collins J, Johnson R, Kitching R, Searle M, Walker R, et al. Effects of simvastatin and enalapril on serum lipoprotein concentrations and left ventricular mass in patients on dialysis. The Perfect Study Collaborative Group. Journal of Nephrology 1997;10(1):33‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Robson R, Collins J, Kitchings R, Searle M, Walker R, Sharpe N, et al. A randomized controlled trial of simvastatin and enalapril in dialysis patients: effects on serum lipoproteins and left ventricular mass [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1994;5(3):526. [CENTRAL: CN‐00550525]
-
- Robson RA, Collins J, Walker RJ, MacMahon S. A randomised controlled trial of simvastatin and enalapril in dialysis patients: effects on serum lipoproteins and left ventricular mass [abstract]. ISN XIII International Congress of Nephrology; 1995 Jul 2‐6; Madrid, Spain. 1995:530. [CENTRAL: CN‐00509440]
-
- Walker RJ, Sutherland WH, Walker H. Simvastatin and cholesteryl ester transfer (CET) activity in renal failure (RF) [abstract]. ISN XIII International Congress of Nephrology; 1995 Jul 2‐6; Madrid, Spain. 1995:529. [CENTRAL: CN‐00509553]
Rojas‐Campos 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rojas‐Campos E, Cortes‐Sanabria L, Martinez‐Ramirez HR, Gonzalez L, Martin‐del‐Campo F, Gonzalez‐Ortiz M, et al. Effect of oral administration of losartan, prazosin, and verapamil on peritoneal solute transport in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2005;25(6):576‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Rojas‐Campos E, Martinez‐Ramirez H, Cortes‐Sanabria L, Camacho R, Martin‐del‐Campo F, Cueto‐Manzano AM. Oral verapamil increases ultrafiltration and peritoneal small solute clearance of CAPD patients [abstract no: SA‐FC130]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2005;16:110A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00583927]
Shigenaga 2009 {published data only}
-
- Shigenaga A, Tamura K, Dejima T, Ozawa M, Wakui H, Masuda S, et al. Effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker on blood pressure variability and cardiovascular remodeling in hypertensive patients on chronic peritoneal dialysis. Nephron Clinical Practice 2009;112(1):c31–c40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Suzuki 2003 {published data only}
-
- Suzuki H, Nakamoto H, Okada H, Sugahara S, Kanno Y. A selective angiotensin receptor antagonist, valsartan, produced regression of left ventricular hypertrophy associated with a reduction of arterial stiffness. Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis 2003;19:59‐66. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Medcalf 2000 {published data only}
-
- Medcalf JF, Carr S, Walls J, Harris KP. The effect of ACE Inhibitors and AII receptor antagonists on erythrocytosis in patients on CAPD taking EPO [abstract]. 37th Congress. European Renal Association. European Dialysis and Transplantation Association; 2000 Sept 17‐20; Nice, France. 2000:235. [CENTRAL: CN‐00461288]
References to ongoing studies
NCT00721773 {published data only}
-
- NCT00721773. Effects of benazepril, valsartan or combination of both on residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis patients. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00721773 (accessed 12 June 2014).
NCT01041963 {published data only}
-
- NCT01041963. The effect of enalapril and losartan on peritoneal membrane in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01041963 (accessed 12 June 2014).
Additional references
Akbari 2009
-
- Akbari A, Knoll G, Ferguson D, McCormick B, Davis A, Biyani M. Angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers in peritoneal dialysis: systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2009;29(5):554–61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bargman 2001
-
- Bargman JM, Thorpe KE, Churchill DN. Relative contribution of residual renal function and peritoneal clearance to adequacy of dialysis: a reanalysis of the CANUSA study. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(10):2158‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Blake 2001
-
- Blake PG. Integrated end‐stage renal disease care: the role of peritoneal dialysis. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2001;16 Suppl 5:61‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cancarini 1986
-
- Cancarini G, Bunori G, Camererini C, Brasa S, Manili L, Maiorca R. Renal function recovery and maintenance of residual diuresis in CAPD and hemodialysis. Peritoneal Dialysis Bulletin 1986;6(2):77‐9. [EMBASE: 1986213696]
Cueto‐Manzano 2003
-
- Cueto‐Manzano AM. Peritoneal dialysis in Mexico. Kidney International 2003;83(Suppl):S90‐2. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fang 2008
-
- Fang W, Oreopoulos DG, Bargman JM. Use of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers and survival in patients on peritoneal dialysis. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2008;23(11):3704‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fenton 1997
-
- Fenton SS, Schaubel DE, Desmeules M, Morrison HI, Mao Y, Copleston P, et al. Hemodialysis versus peritoneal dialysis: a comparison of adjusted mortality rates. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1997;30(3):334‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gokal 1999
-
- Gokal R, Figueras M, Olle A, Rovira J, Badia X. Outcomes in peritoneal dialysis and haemodialysis‐a comparative assessment of survival and quality of life. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1999;14 Suppl 6:24‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Heaf 2002
-
- Heaf JG, Lokkegaard H, Madsen M. Initial survival advantage of peritoneal dialysis relative to haemodialysis. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2002;17(1):112‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Herget‐Rosenthal 2012
-
- Herget‐Rosenthal S, Ostrowski M, Kribben A. Definition and risk factors of rapidly declining residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis: an observational study. Kidney & Blood Pressure Research 2012;35(4):233‐41. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Kolesnyk 2007
-
- Kolesnyk I, Dekker FW, Noordzij M, Cessie S, Struijk DG, Krediet RT. Impact of ACE inhibitors and AII receptor blockers on peritoneal membrane transport characteristics in long‐term peritoneal dialysis patients. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2007;27(4):446‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Li 1999
-
- Li PK, Szeto CC, Law MC, Chau KF, Fung KS, Leung CB, et al. Comparison of double‐bag and Y‐set disconnect systems in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: a randomized prospective multicenter study. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1999;33(3):535‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Li 2001a
-
- Li PK, Szeto CC. Adequacy targets of peritoneal dialysis in the Asian population. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2001;21 Suppl 3:S378‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Li 2001b
-
- Li LP, Chow KM. The cost barrier to peritoneal dialysis in the developing world‐an Asian perspective. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2001;2001(21 Suppl 3):S307‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Maiorca 1995
-
- Maiorca R, Brunori G, Zubani R, Cancarini GC, Manili L, Camerini C, et al. Predictive value of dialysis adequacy and nutritional indices for mortality and morbidity in CAPD and HD patients. A longitudinal study. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1995;10(12):2295‐305. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Moist 2000
-
- Moist LM, Port FK, Orzol SM, Young EW, Ostbye T, Wolfe RA, et al. Predictors of loss of residual renal function among new dialysis patients. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2000;11(3):556‐64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Patel 2014
Schaubel 2000
-
- Schaubel DE, Fenton SS. Trends in mortality on peritoneal dialysis: Canada. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2000;11(1):126‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shafi 2010
-
- Shafi T, Jaar BG, Plantinga LC, Fink NE, Sadler JH, Parekh RS, et al. Association of residual urine output with mortality, quality of life, and inflammation in incident hemodialysis patients: the Choices for Healthy Outcomes in Caring for End‐Stage Renal Disease (CHOICE) Study. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2010;56(2):348‐58. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Shemin 2000
-
- Shemin D, Bostom AG, Lambert C, Hill C, Kitsen J, Kliger AS. Residual renal function in a large cohort of peritoneal dialysis patients: change over time, impact on mortality and nutrition. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2000;20(4):439‐44. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Suzuki 2003a
-
- Suzuki H, Nakamoto H, Okada H, Sugahara S, Kanno Y. A selective angiotensin receptor antagonist, Valsartan, produced regression of left ventricular hypertrophy associated with a reduction of arterial stiffness. Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis 2003;19:59‐66. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Suzuki 2003b
-
- Suzuki T, Kanno Y, Nakamoto N, Okada H, Sugahara S, Suzuki H. Peritoneal dialysis versus hemodialysis: A five‐year comparison of survival and effects on the cardiovascular system, erythropoiesis, and calcium metabolism. Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis 2003;19:148‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Szeto 2000
-
- Szeto CC, Wong TY, Leung CB, Wang AY, Law MC, Lui SF, et al. Importance of dialysis adequacy in mortality and morbidity of Chinese CAPD patients. Kidney International 2000;58(1):400‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Termorshuizen 2003
-
- Termorshuizen F, Korevaar JC, Dekker FW, Manen JG, Boeschoten EW, Krediet RT. Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis: comparison of adjusted mortality rates according to the duration of dialysis: analysis of The Netherlands Cooperative Study on the Adequacy of Dialysis. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2003;14(11):2851‐60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
USRDS 2003
-
- US Renal Data System. USRDS 2003 annual report: atlas of end‐stage renal disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD, 2003. http://www.usrds.org/atlas03.aspx (accessed 12 June 2014):78‐80.
Venkataraman 2000
-
- Venkataraman V, Nolph KD. Preservation of residual renal function‐an important goal. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2000;20(4):392‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Williams 2002
-
- Williams JD, Craig KJ, Topley N, Ruhland C, Fallon M, Newman GR, et al. Morphologic changes in the peritoneal membrane of patients with renal disease. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2002;13(2):470‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Zhang 2011
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

