Computational analysis of the effectiveness of blood flushing with saline injection from an intravascular diagnostic catheter
- PMID: 24953876
- PMCID: PMC4429308
- DOI: 10.1002/cnm.2657
Computational analysis of the effectiveness of blood flushing with saline injection from an intravascular diagnostic catheter
Abstract
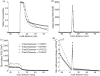
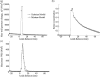
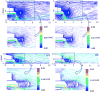
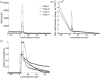
Optical techniques including fluorescence lifetime spectroscopy have demonstrated potential as a tool for study and diagnosis of arterial vessel pathologies. However, their application in the intravascular diagnostic procedures has been hampered by the presence of blood hemoglobin that affects the light delivery to and the collection from the vessel wall. We report a computational fluid dynamics model that allows for the optimization of blood flushing parameters in a manner that minimizes the amount of saline needed to clear the optical field of view and reduces any adverse effects caused by the external saline jet. A 3D turbulence (k - ω) model was employed for Eulerian-Eulerian two-phase flow to simulate the flow inside and around a side-viewing fiber-optic catheter. Current analysis demonstrates the effects of various parameters including infusion and blood flow rates, vessel diameters, and pulsatile nature of blood flow on the flow structure around the catheter tip. The results from this study can be utilized in determining the optimal flushing rate for given vessel diameter, blood flow rate, and maximum wall shear stress that the vessel wall can sustain and subsequently in optimizing the design parameters of optical-based intravascular catheters.
Keywords: Eulerian-Eulerian two-phase flow; k − ω turbulence model; mixture model; multiphase flow.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Drexler W, Morgner U, Kartner FX, Pitris C, Boppart SA, Li XD, Ippen EP, Fujimoto JG. In vivo ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence. Optics Letters. 1999;24(17):1221–1223. - PubMed
-
- Cheng H, Luo Q, Zeng S, Chen S, Cen J, Gong H. Modified laser speckle imaging method with improved spatial resolution. Journal of Biomedical Optics. 2003;8(3):559–564. - PubMed
-
- Kolkman RGM, Hondebrink E, Steenbergen W. In vivo photoacoustic imaging of blood vessels using an extreme-narrow aperture sensor. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics. 2003;9(2):343–346.
-
- Xu M, Wang LV. Photoacoustic imaging in biomedicine. Review of Scientific Instruments. 2006;77(4):041101–22.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

