Do stimulant medications improve educational and behavioral outcomes for children with ADHD?
- PMID: 24954077
- PMCID: PMC4815037
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhealeco.2014.05.002
Do stimulant medications improve educational and behavioral outcomes for children with ADHD?
Abstract
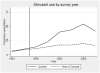
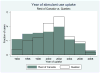
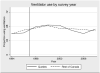
We examine the effects of a policy change in the province of Quebec, Canada which greatly expanded insurance coverage for prescription medications. We show that the change was associated with a sharp increase in the use of stimulant medications commonly prescribed for ADHD in Quebec relative to the rest of Canada. We ask whether this increase in medication use was associated with improvements in emotional functioning or academic outcomes among children with ADHD. We find little evidence of improvement in either the medium or the long run. Our results are silent on the effects on optimal use of medication for ADHD, but suggest that expanding medication in a community setting had little positive benefit and may have had harmful effects given the average way these drugs are used in the community.
Keywords: ADHD; Children's mental health; Prescription drug coverage; Ritalin; Stimulants.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparison of ritalin and adderall: efficacy and time-course in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.Pediatrics. 1999 Apr;103(4):e43. doi: 10.1542/peds.103.4.e43. Pediatrics. 1999. PMID: 10103335 Clinical Trial.
-
Are stimulants overprescribed? Treatment of ADHD in four U.S. communities.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1999 Jul;38(7):797-804. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199907000-00008. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1999. PMID: 10405496
-
Antipsychotic Treatment Among Youths With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Jul 3;2(7):e197850. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.7850. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31348506 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Council on Scientific Affairs, American Medical Association.JAMA. 1998 Apr 8;279(14):1100-7. doi: 10.1001/jama.279.14.1100. JAMA. 1998. PMID: 9546570 Review.
-
The Effects of Long-Acting Stimulant and Nonstimulant Medications in Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2018 Oct;28(8):494-507. doi: 10.1089/cap.2017.0151. Epub 2018 Jun 13. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29897263 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of public hospital pricing reform on medical expenditure structure in Jiangsu, China: a synthetic control analysis.BMC Health Serv Res. 2019 Jul 23;19(1):512. doi: 10.1186/s12913-019-4357-x. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019. PMID: 31337396 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Effects of Pharmacological, Psychosocial, and Alternative/Complementary Interventions in Children and Adolescents With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Meta-Regression Approach.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021 Oct 23;24(10):776-786. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyab034. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34086891 Free PMC article.
-
Universal Pharmacare and Contraceptive Dispensations Among Youth.JAMA Pediatr. 2025 Aug 18:e252585. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2025.2585. Online ahead of print. JAMA Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40824678 Free PMC article.
-
Medical treatment of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and children's academic performance.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 29;13(11):e0207905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207905. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30496240 Free PMC article.
-
Overdiagnosis of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Scoping Review.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Apr 1;4(4):e215335. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.5335. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 33843998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aizer A. Peer Effects, Institutions, and Human Capital Accumulation: The Externalities of ADD. NBER Working Paper # 14354. 2009
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th. 1994.
-
- Baker Michael, Gruber Jonathan, Milligan Kevin. Journal of Political Economy. 4. Vol. 116. University of Chicago Press; 2008. Universal Child Care, Maternal Labor Supply, and Family Well-Being; pp. 709–745.
-
- Barbaresi WJ, Katusic SK, Colligan RC, Weaver AL, Jacobsen SJ. Modifiers of Long-Term School Outcomes for Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Does Treatment with Stimulant Medication Make a Difference? Results from a Population Based Study. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 28(4):2007, 274–287. - PubMed
-
- Bedard A, Jain U, Johnson SH, Tannock R. Effects of Methylphenidate on Working Memory Components: Influence of Measurement. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2007;28(9):872–880. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical