Diurnal variation of gait in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: The DIVIGN study
- PMID: 24954102
- PMCID: PMC4166456
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2014.05.009
Diurnal variation of gait in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: The DIVIGN study
Abstract
Background: Circadian variation of joint stiffness (morning stiffness) and its impact on functional ability are widely recognised in rheumatoid arthritis. Subsequent within-day variation of walking ability is important due to the increased availability of instrumented gait analysis. This study aimed to quantify diurnal variation of gait in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and explore associations with disease characteristics.
Methods: Thirty one inpatients with rheumatoid arthritis walked at a self-selected speed along a GAITRite instrumented walkway 5 times during a single day.
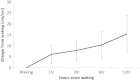
Findings: Participants showed marked diurnal variation in gait, leading to a systematic variation throughout the day (F=19.56, P=<0.001). Gait velocity and stride length both increased, whereas the proportion of each gait cycle spent in stance phase or double support decreased, consistent with improving function throughout the day. Although absolute gait velocity correlated with disease characteristics, the magnitude of diurnal variation appeared to be independent of disease activity (rho=0.26, P=0.15), disease duration (rho=-0.19, P=0.324), and underlying functional ability (rho=0.09, P=0.65).
Interpretation: Although morning stiffness is well recognised in rheumatoid arthritis, this is the first time that its effect on gait has been quantified. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis exhibited a systematic change in walking ability throughout the day, which was independent of disease characteristics. These findings have important implications for the interpretation of existing data and the design of future studies. Repeat measures should be conducted at the same time of day to exclude the effects of diurnal variation.
Keywords: Diurnal variation; Gait analysis; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Concurrent validation of activity monitors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2013 Apr;28(4):473-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2013.02.009. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2013. PMID: 23522723 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Concurrent Validity of the Zeno Walkway for Measuring Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters in Older Adults.J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2019 Jul/Sep;42(3):E42-E50. doi: 10.1519/JPT.0000000000000168. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2019. PMID: 29286982
-
Gait patterns in subjects with rheumatoid arthritis cannot be explained by reduced speed alone.Gait Posture. 2009 Apr;29(3):499-503. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2008.11.010. Epub 2009 Jan 3. Gait Posture. 2009. PMID: 19121943
-
How should morning function in rheumatoid arthritis be assessed? Bibliographic study of current assessment.Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 2011;125:17-22. doi: 10.3109/03009742.2011.566436. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 2011. PMID: 21529306 Review.
-
The role of the circadian clock in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2013 Feb 21;15(1):205. doi: 10.1186/ar4146. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 23427807 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aletaha D., Smolen J., Ward M.M. Measuring function in rheumatoid arthritis: identifying reversible and irreversible components. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2784–2792. - PubMed
-
- Barkham N., Coates L.C., Keen H., Hensor E.M.A., Fraser A., Redmond A.C., Cawkwell L., Emery P. Double-blind placebo-controlled trial of etanercept in the prevention of work disability in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010;69:1926–1928. - PubMed
-
- Bellace J.V., Healy D., Besser M.P., Byron T., Hohman L. Validity of the Dexter Evaluation System's Jamar dynamometer attachment for assessment of hand grip strength in a normal population. J. Hand Ther. 2000;13:46–51. - PubMed
-
- Conrad K.J., Budiman-Mak E., Roach K.E., Hedeker D. Impacts of foot orthoses on pain and disability in rheumatoid arthritics. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1996;49:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical