The cholesterol metabolite 27-hydroxycholesterol promotes atherosclerosis via proinflammatory processes mediated by estrogen receptor alpha
- PMID: 24954418
- PMCID: PMC4098728
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.05.013
The cholesterol metabolite 27-hydroxycholesterol promotes atherosclerosis via proinflammatory processes mediated by estrogen receptor alpha
Abstract
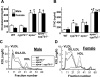
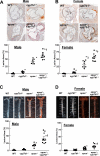
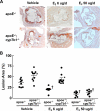
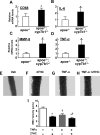
Oxysterols are cholesterol metabolites that serve multiple functions in lipid metabolism, including as liver X receptor (LXR) ligands. 27-hydroxycholesterol (27HC) is an abundant oxysterol metabolized by CYP7B1. How 27HC impacts vascular health is unknown. We show that elevations in 27HC via cyp7b1 deletion promote atherosclerosis in apoe(-/-) mice without altering lipid status; furthermore, estrogen-related atheroprotection is attenuated. In wild-type mice, leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion is increased by 27HC via estrogen receptor (ER)-dependent processes. In monocytes/macrophages, 27HC upregulates proinflammatory genes and increases adhesion via ERα. In endothelial cells, 27HC is also proadhesive via ERα, and in contrast to estrogen, which blunts NF-κB activation, 27HC stimulates NF-κB activation via Erk1,2 and JNK-dependent IκBα degradation. Whereas 27HC administration to apoe(-/-) mice increases atherosclerosis, apoe(-/-);erα(-/-) are unaffected. Thus, 27HC promotes atherosclerosis via proinflammatory processes mediated by ERα, and it attenuates estrogen-related atheroprotection. Strategies to lower 27HC may complement approaches targeting cholesterol to prevent vascular disease.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
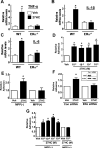
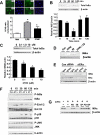
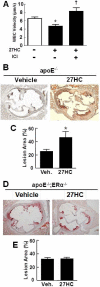
Similar articles
-
Macrophage-to-endothelial cell crosstalk by the cholesterol metabolite 27HC promotes atherosclerosis in male mice.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 25;14(1):4101. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39586-z. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37491347 Free PMC article.
-
Role of reactive oxygen species in regulating 27-hydroxycholesterol-induced apoptosis of hematopoietic progenitor cells and myeloid cell lines.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Oct 31;13(10):916. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05360-0. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36316327 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-opposed inflammatory effects of 27-hydroxycholesterol are mediated via differences in estrogen signaling.J Pathol. 2020 Aug;251(4):429-439. doi: 10.1002/path.5477. Epub 2020 Jul 7. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32472585 Free PMC article.
-
27-Hydroxycholesterol, an endogenous selective estrogen receptor modulator.Maturitas. 2017 Oct;104:29-35. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2017.07.014. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Maturitas. 2017. PMID: 28923174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Re-adopting classical nuclear receptors by cholesterol metabolites.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Mar;157:20-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.11.002. Epub 2015 Nov 10. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26563834 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lovastatin reversed the enhanced sphingomyelin caused by 27-hydroxycholesterol in cultured vascular endothelial cells.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2015 Dec 3;5:127-133. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2015.11.024. eCollection 2016 Mar. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2015. PMID: 28955814 Free PMC article.
-
A theory of eu-estrogenemia: a unifying concept.Menopause. 2017 Sep;24(9):1086-1097. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000000895. Menopause. 2017. PMID: 28562489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Contribution of Cholesterol and Its Metabolites to the Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer.Horm Cancer. 2016 Aug;7(4):219-28. doi: 10.1007/s12672-016-0262-5. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Horm Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27020054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
27-Hydroxycholesterol acts on estrogen receptor α expressed by POMC neurons in the arcuate nucleus to modulate feeding behavior.Sci Adv. 2024 Jul 12;10(28):eadi4746. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi4746. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38996023 Free PMC article.
-
27-Hydroxycholesterol acts on myeloid immune cells to induce T cell dysfunction, promoting breast cancer progression.Cancer Lett. 2020 Nov 28;493:266-283. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.08.020. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32861706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnal JF, Laurell H, Fontaine C, Billon A, Calippe B, Lenfant F, Gourdy P. Estrogen receptor actions on vascular biology and inflammation: implications in vascular pathophysiology. Climacteric. 12 Suppl. 2009;1:12–17. - PubMed
-
- Billon-Gales A, Fontaine C, Douin-Echinard V, Delpy L, Berges H, Calippe B, Lenfant F, Laurell H, Guery JC, Gourdy P, Arnal JF. Endothelial estrogen receptor-alpha plays a crucial role in the atheroprotective action of 17beta-estradiol in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Circulation. 2009;120:2567–2576. - PubMed
-
- Brown AJ, Jessup W. Oxysterols and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1999;142:1–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

