The PI3K/Akt signal hyperactivates Eya1 via the SUMOylation pathway
- PMID: 24954506
- PMCID: PMC4275428
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2014.179
The PI3K/Akt signal hyperactivates Eya1 via the SUMOylation pathway
Abstract
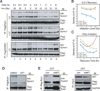
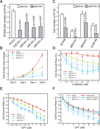
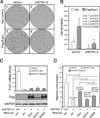
Eyes absent 1 (Eya1) is a conserved critical regulator of organ-specific stem cells. Ectopic Eya1 activities, however, promote transformation of mammary epithelial cells. Signals that instigate Eya1 oncogenic activities remain to be determined. Here, we show that Akt1 kinase physically interacts with Eya1 and phosphorylates a conserved consensus site of the Akt kinase. PI3K/Akt signaling enhances Eya1 transcription activity, which largely attributes to the phosphorylation-induced reduction of Eya1 SUMOylation. Indeed, SUMOylation inhibits Eya1 transcription activity; and pharmacologic and genetic activation of PI3K/Akt robustly reduces Eya1 SUMOylation. Wild-type but not Akt phosphorylation site mutant Eya1 variant rescues the cell migratory phenotype of EYA1-silenced breast cancer cells, highlighting the importance of Eya1 phosphorylation. Furthermore, knockdown EYA1 sensitizes breast cancer cells to the PI3K/Akt1 inhibitor and irradiation treatments. Thus, the PI3K/Akt signal pathway activates Eya1. These findings further suggest that regulation of SUMOylation by PI3K/Akt signaling is likely an important aspect of tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare that they have no conflict interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The canonical wnt signal restricts the glycogen synthase kinase 3/fbw7-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of eya1 phosphatase.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Jul;34(13):2409-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00104-14. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24752894 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-101 inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting EYA1 in breast cancer.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Jun;37(6):1643-51. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2557. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27082308
-
EYA1 phosphatase function is essential to drive breast cancer cell proliferation through cyclin D1.Cancer Res. 2013 Jul 15;73(14):4488-99. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4078. Epub 2013 May 1. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23636126 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between STAT5 activation and PI3K/AKT functions in normal and transformed mammary epithelial cells.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Aug 15;451:31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.04.025. Epub 2017 May 8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28495456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of protein tyrosine phosphatases in cancer.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2006;81:297-329. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6603(06)81008-1. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16891175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The retinal determination gene network: from developmental regulator to cancer therapeutic target.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 2;7(31):50755-50765. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9394. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27203207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-assembling peptides induced by eyes absent enzyme to boost the efficacy of doxorubicin therapy in drug-resistant breast cancer cells.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 25;10(13):e33629. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33629. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39071664 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometry-based detection and assignment of protein posttranslational modifications.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Jan 16;10(1):63-71. doi: 10.1021/cb500904b. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25541750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Tensile Frequency on the Osteogenic Differentiation of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Jul 2;15:5957-5971. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S368394. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35811779 Free PMC article.
-
MES23.5 DA Immortalized Neuroblastoma Cells Self-protect Against Early Injury by Overexpressing Glial Cell-derived Neurotrophic Factor via Akt1/Eya1/Six2 Signaling.J Mol Neurosci. 2020 Mar;70(3):328-339. doi: 10.1007/s12031-019-01416-7. Epub 2019 Nov 13. J Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31720997
References
-
- Li X, Oghi KA, Zhang J, Krones A, Bush KT, Glass CK, et al. Eya protein phosphatase activity regulates Six1-Dach-Eya transcriptional effects in mammalian organogenesis. Nature. 2003;426:247–254. - PubMed
-
- Tootle TL, Silver SJ, Davies EL, Newman V, Latek RR, Mills IA, et al. The transcription factor Eyes absent is a protein tyrosine phosphatase. Nature. 2003;426:299–302. - PubMed
-
- Rayapureddi JP, Kattamuri C, Steinmetz BD, Frankfort BJ, Ostrin EJ, Mardon G, et al. Eyes absent represents a class of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Nature. 2003;426:295–298. - PubMed
-
- Okabe Y, Sano T, Nagata S. Regulation of the innate immune response by threonine-phosphatase of Eyes absent. Nature. 2009;460:520–524. - PubMed
-
- Abate-Shen C. Deregulated homeobox gene expression in cancer: cause or consequence? Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:777–785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

