Imaging mouse lung allograft rejection with (1)H MRI
- PMID: 24954886
- PMCID: PMC4272671
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.25313
Imaging mouse lung allograft rejection with (1)H MRI
Abstract
Purpose: To demonstrate that longitudinal, noninvasive monitoring via MRI can characterize acute cellular rejection in mouse orthotopic lung allografts.
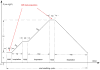
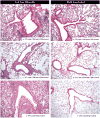
Methods: Nineteen Balb/c donor to C57BL/6 recipient orthotopic left lung transplants were performed, further divided into control-Ig versus anti-CD4/anti-CD8 treated groups. A two-dimensional multislice gradient-echo pulse sequence synchronized with ventilation was used on a small-animal MR scanner to acquire proton images of lung at postoperative days 3, 7, and 14, just before sacrifice. Lung volume and parenchymal signal were measured, and lung compliance was calculated as volume change per pressure difference between high and low pressures.
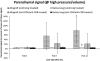
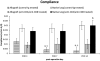
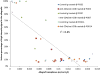
Results: Normalized parenchymal signal in the control-Ig allograft increased over time, with statistical significance between day 14 and day 3 posttransplantation (0.046→0.789; P < 0.05), despite large intermouse variations; this was consistent with histopathologic evidence of rejection. Compliance of the control-Ig allograft decreased significantly over time (0.013→0.003; P < 0.05), but remained constant in mice treated with anti-CD4/anti-CD8 antibodies.
Conclusion: Lung allograft rejection in individual mice can be monitored by lung parenchymal signal changes and by lung compliance through MRI. Longitudinal imaging can help us better understand the time course of individual lung allograft rejection and response to treatment.
Keywords: MRI; acute cellular rejection; compliance; lung transplant.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
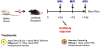


References
-
- Kotloff RM, Thabut G. Lung transplantation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;184(2):159–171. - PubMed
-
- Christie JD, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, et al. The registry of the international society for heart and lung transplantation: 29th adult lung and heart-lung transplant report-2012. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2012;31(10):1073–1086. - PubMed
-
- Belperio JA, Weigt SS, Fishbein MC, Lynch JP., 3rd Chronic lung allograft rejection: Mechanisms and therapy. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009;6(1):108–121. - PubMed
-
- Todd JL, Palmer SM. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome: The final frontier for lung transplantation. Chest. 2011;140(2):502–508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

