Identification of SNP barcode biomarkers for genes associated with facial emotion perception using particle swarm optimization algorithm
- PMID: 24955105
- PMCID: PMC4050220
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-859X-13-15
Identification of SNP barcode biomarkers for genes associated with facial emotion perception using particle swarm optimization algorithm
Abstract
Background: Facial emotion perception (FEP) can affect social function. We previously reported that parts of five tested single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the MET and AKT1 genes may individually affect FEP performance. However, the effects of SNP-SNP interactions on FEP performance remain unclear.
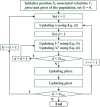
Methods: This study compared patients with high and low FEP performances (n = 89 and 93, respectively). A particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm was used to identify the best SNP barcodes (i.e., the SNP combinations and genotypes that revealed the largest differences between the high and low FEP groups).
Results: The analyses of individual SNPs showed no significant differences between the high and low FEP groups. However, comparisons of multiple SNP-SNP interactions involving different combinations of two to five SNPs showed that the best PSO-generated SNP barcodes were significantly associated with high FEP score. The analyses of the joint effects of the best SNP barcodes for two to five interacting SNPs also showed that the best SNP barcodes had significantly higher odds ratios (2.119 to 3.138; P < 0.05) compared to other SNP barcodes. In conclusion, the proposed PSO algorithm effectively identifies the best SNP barcodes that have the strongest associations with FEP performance.
Conclusions: This study also proposes a computational methodology for analyzing complex SNP-SNP interactions in social cognition domains such as recognition of facial emotion.
Keywords: Algorithm; Facial emotion perception; Particle swarm optimization; SNP interaction; Single-nucleotide polymorphism.
Similar articles
-
An improved PSO algorithm for generating protective SNP barcodes in breast cancer.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37018. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037018. Epub 2012 May 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22623973 Free PMC article.
-
Particle swarm optimization algorithm for analyzing SNP-SNP interaction of renin-angiotensin system genes against hypertension.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Jul;40(7):4227-33. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2504-8. Epub 2013 May 22. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23695493
-
A comparative analysis of chaotic particle swarm optimizations for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism barcodes.Artif Intell Med. 2016 Oct;73:23-33. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Artif Intell Med. 2016. PMID: 27926379
-
Application of particle swarm optimization to water management: an introduction and overview.Environ Monit Assess. 2020 Apr 13;192(5):281. doi: 10.1007/s10661-020-8228-z. Environ Monit Assess. 2020. PMID: 32285219 Review.
-
Patterns of impaired social cognition in children and adolescents with epilepsy: The borders between different epilepsy phenotypes.Epilepsy Behav. 2019 Nov;100(Pt B):106146. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.01.031. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Epilepsy Behav. 2019. PMID: 30894295 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of High-Order Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Barcodes in Breast Cancer Using a Hybrid Taguchi-Genetic Algorithm: Case-Control Study.JMIR Med Inform. 2020 Jun 17;8(6):e16886. doi: 10.2196/16886. JMIR Med Inform. 2020. PMID: 32554381 Free PMC article.
-
Application of simulation-based CYP26 SNP-environment barcodes for evaluating the occurrence of oral malignant disorders by odds ratio-based binary particle swarm optimization: A case-control study in the Taiwanese population.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 29;14(8):e0220719. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220719. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31465460 Free PMC article.
-
Multiomics with Evolutionary Computation to Identify Molecular and Module Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Complex Disease.Genes (Basel). 2025 Feb 20;16(3):244. doi: 10.3390/genes16030244. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149396 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pinkham AE, Penn DL, Perkins DO, Graham KA, Siegel M. Emotion perception and social skill over the course of psychosis: a comparison of individuals "at-risk" for psychosis and individuals with early and chronic schizophrenia spectrum illness. Cogn Neuropsychiatry. 2007;13(3):198–212. doi: 10.1080/13546800600985557. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous