A novel fluid resuscitation protocol: provide more protection on acute kidney injury during septic shock in rats
- PMID: 24955162
- PMCID: PMC4057841
A novel fluid resuscitation protocol: provide more protection on acute kidney injury during septic shock in rats
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the therapeutic effects of a novel fluid resuscitation protocol (early fluid resuscitation plus 2% hydrogen inhalation) on acute kidney injury during septic shock induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats.
Methods: Sixty male Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups (n = 15 per group): control group (C), septic shock group (S), septic shock with early fluid resuscitation group (R), and septic shock with early fluid resuscitation plus 2% hydrogen inhalation group (R+R+H2). The rats were ventilated, and a 2% hydrogen mixture was used in Group R+H2. Lipopolysaccharide (10 mg/kg) was administered to establish the septic shock model in rats and fluid resuscitation was performed in Groups R and R+R+H2.
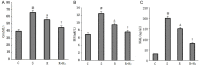
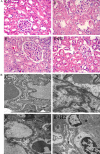
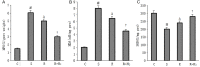
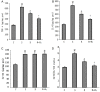
Results: Fluid resuscitation with 2% hydrogen inhalation decreased serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. It also reduced oxidative stress injury and decreased renal tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6 levels compared with fluid resuscitation alone.
Conclusion: Early fluid resuscitation plus 2% hydrogen inhalation provided more protection against AKI during septic shock.
Keywords: Septic shock; acute kidney injury; fluid resuscitation; hydrogen inhalation; inflammation; oxidative stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined early fluid resuscitation and hydrogen inhalation attenuates lung and intestine injury.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan 28;19(4):492-502. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i4.492. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23382627 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of different fluid resuscitation on renal function and glycocalyx in septic shock rats].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Jun 1;60(6):552-555. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20200628-00626. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34058812 Chinese.
-
Effect of early fluid resuscitation on the lung in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced septic shock.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Jan;17(2):161-9. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23377803
-
Acute Kidney Injury and Fluid Resuscitation in Septic Patients: Are We Protecting the Kidney?Nephron. 2019;143(3):170-173. doi: 10.1159/000501748. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Nephron. 2019. PMID: 31394531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012.Crit Care Med. 2013 Feb;41(2):580-637. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af. Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23353941
Cited by
-
Molecular hydrogen: a preventive and therapeutic medical gas for various diseases.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 21;8(60):102653-102673. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21130. eCollection 2017 Nov 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29254278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic effect of hydrogen and its mechanisms in kidney disease treatment.Med Gas Res. 2024 Apr-Jun;14(2):48-53. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.378880. Med Gas Res. 2024. PMID: 37929507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Use and Treatment Mechanism of Molecular Hydrogen in the Treatment of Various Kidney Diseases including Diabetic Kidney Disease.Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 17;11(10):2817. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102817. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Hydrogen Therapy Ameliorates Organ Damage Induced by Sepsis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:5806057. doi: 10.1155/2016/5806057. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 27413421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevention of lipopolysaccharide-induced CD11b+ immune cell infiltration in the kidney: role of AT2 receptors.Biosci Rep. 2019 May 23;39(5):BSR20190429. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190429. Print 2019 May 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31072913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence outcome and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1368–1377. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
