Cardiac ablation of Rheb1 reduces sodium currents in infant mice
- PMID: 24955166
- PMCID: PMC4057845
Cardiac ablation of Rheb1 reduces sodium currents in infant mice
Abstract
Objective: The Ras homolog enriched in brain gene (Rheb) is a center player within the insulin/Rheb/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) pathway, and plays a critical role in regulating cellular growth. Rheb-/- embryos have been reported to die around midgestation, due to the defects of the development of the cardiovascular system. Recent studies from ours and another group consistently showed that Rheb1 was indispensable for the cardiac hypertrophic growth after early postnatal period. Besides that, we also found that Rheb1 a-MHC-Cre (cKO) mice exhibited ventricular tachycardia. However, the precise mechanism by which Rheb1 knockout causes ventricular arrhythmia in these mice is still unclear.
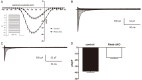
Methods: Mouse cardiomyocytes were isolated using 10 days suckling Rheb1 cKO and wide type mice using Collagenase Type II. Sodium currents and L-type calcium currents were recorded using the whole-cell patch clamping technique.
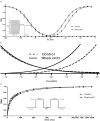
Results: The sodium current density of ventricular cardiomyocytes from Rheb1 cKO mice was decreased by about 60%. Significant left shift but no slope altered was observed in activation curve with V1/2 values of -35.35 ± 1.12 mV for Rheb1 cKO group and -40.72 ± 1.18 mV for the controls. In addition, the area of window current, which refers the overlap of normalized activation and inactivation, was larger in Rheb1 cKO mice. Moreover, the sodium current, in general, was recovered much slower in Rheb1 cKO mice than that of the controls. However, L-type calcium currents were preserved in Rheb1 cKO mice.
Conclusion: Sodium currents are decreased in Rheb1 cKO mice, which might be responsible for the phenotype of arrhythima in Rheb1 cKO mice. Understanding the molecular composition of sodium ion channel complexes in the heart of these Rheb1 cKO mice will be critical to develop innovative and effective therapies for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmia.
Keywords: Arrhythmia; L-type calcium currents; Rheb1; patch clamp; sodium currents.
Figures

References
-
- Bonneau A, Parmar N. Effects of RhebL1 silencing on the mTOR pathway. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39:2129–2137. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, Tao L, Shen S, Xiao J, Wu H, Li B, Wu X, Luo W, Xiao Q, Hu X, Liu H, Nie J, Lu S, Yuan B, Han Z, Xiao B, Yang Z, Li X. Cardiac ablation of Rheb1 induces impaired heart growth, endoplasmic reticulum-associated apoptosis and heart failure in infant mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:24380–24398. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tamai T, Yamaguchi O, Hikoso S, Takeda T, Taneike M, Oka T, Oyabu J, Murakawa T, Nakayama H, Uno Y, Horie K, Nishida K, Sonenberg N, Shah AM, Takeda J, Komuro I, Otsu K. Rheb (Ras homologue enriched in brain)-dependent mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) activation becomes indispensable for cardiac hypertrophic growth after early postnatal period. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:10176–10187. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
