Pancreatic cystic lesions: The value of contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound to influence the clinical pathway
- PMID: 24955342
- PMCID: PMC4064160
- DOI: 10.4103/2303-9027.131040
Pancreatic cystic lesions: The value of contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound to influence the clinical pathway
Abstract
Background and objectives: Cystic pancreatic lesions are a growing diagnostic challenge. The aim of this study was to proof a new diagnostic concept based on contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound (CE-EUS) for differential diagnosis.
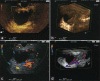
Patients and methods: A total of 125 patients with unclear cystic pancreatic lesions were included. The initial diagnostic was made by CE-EUS dividing the lesions in a group without contrast enhancing effect in the cystic wall, septae or nodule indicating pseudocysts or dysontogenetic cysts and a group with contrast enhancing effect in the described structures indicating cystic neoplasias. The investigations were performed using a Pentax echoendoscope and Hitachi Preirus ultrasound machine. The contrast enhancer used was 4.8 mL SonoVue(®) (Bracco, Italy). The group with suspected cystic neoplasia was referred for endoscopic fine-needle puncture for further diagnostic or treatment decisions.
Results: The dividing of the groups by contrast-enhanced ultrasound was feasible because all (n = 56) suspected cystic neoplasias showed a contrast enhancing effect, whereas in only 4 from 69 pseudocystic or dysontogenetic cystic lesions a contrast enhancing effect in the wall could be observed. Endoscopic fine-needle puncture could diagnose all malignant neoplasias and relevant premalignant conditions. The long-term follow-up did not show any development of malignant cystic lesions.
Conclusion: Using CE-EUS and endoscopic fine-needle puncture as diagnostic criteria seemed to be a feasible method to deal with different cystic lesions in daily practice.
Keywords: Cystic lesion; diagnosis; endoscopic ultrasound; microbubble; pancreas; puncture.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Zaheer A, Pokharel SS, Wolfgang C, et al. Incidentally detected cystic lesions of the pancreas on CT: Review of literature and management suggestions. Abdom Imaging. 2013;38:331–41. - PubMed
-
- Scoazec JY, Vullierme MP, Barthet M, et al. Cystic and ductal tumors of the pancreas: Diagnosis and management. J Visc Surg. 2013;150:69–84. - PubMed
-
- Kim SC, Song KB, Jung YS, et al. Short-term clinical outcomes for 100 consecutive cases of laparoscopic pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy: Improvement with surgical experience. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:95–103. - PubMed
-
- Hocke M, Dietrich C. Contrast-enhanced sonography and endoscopic ultrasound for the diagnosis of pancreatic diseases. Zentralbl Chir. 2013 Oct 16; [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Hocke M, Ignee A, Dietrich CF. Advanced endosonographic diagnostic tools for discrimination of focal chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma - Elastography, contrast enhanced high mechanical index (CEHMI) and low mechanical index (CELMI) endosonography in direct comparison. Z Gastroenterol. 2012;50:199–203. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

