Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effect of Bauhinia hookeri extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice and characterization of its bioactive compounds by HPLC-PDA-ESI-MS/MS
- PMID: 24955350
- PMCID: PMC4053259
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/245171
Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effect of Bauhinia hookeri extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice and characterization of its bioactive compounds by HPLC-PDA-ESI-MS/MS
Abstract
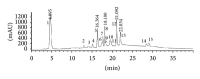
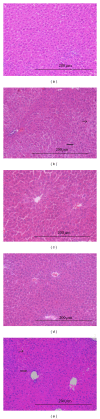
The hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of Bauhinia hookeri ethanol extract (BHE) against CCl4-induced liver injury was investigated in mice. BHE was administered (500 and 1000 mg/kg/day) along with CCl4 for 6 weeks. The hepatic marker enzymes: alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were determined in the serum. The antioxidant parameters: glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione transferase (GST), and malondialdehyde (MDA) were estimated in the liver homogenate. BHE treatment significantly inhibited the CCl4-induced increase in ALT (44 and 64%), AST (36 and 46%), ALP (28 and 42%), and MDA (39 and 51%) levels at the tested doses, respectively. Moreover, BHE treatment markedly increased the activity of antioxidant parameters GSH, GPx, GR, GST, and SOD. Histological observations confirmed the strong hepatoprotective activity. These results suggest that a dietary supplement of BHE could exert a beneficial effect against oxidative stress and various liver diseases by enhancing the antioxidant defense status, reducing lipid peroxidation, and protecting against the pathological changes of the liver. The hepatoprotective activity of BHE is mediated, at least in part, by the antioxidant effect of its constituents. The active constituents of BHE were identified by HPLC-PDA-ESI/MS/MS.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of Melaleuca styphelioides on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice.Pharm Biol. 2014 Dec;52(12):1581-90. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2014.908398. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Pharm Biol. 2014. PMID: 25243881
-
Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of Fagonia schweinfurthii (Hadidi) Hadidi extract in carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cell line and rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Dec 12;150(3):973-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.09.048. Epub 2013 Oct 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24140589
-
Hepatoprotective effect of Scoparia dulcis on carbon tetrachloride induced acute liver injury in mice.Am J Chin Med. 2010;38(4):761-75. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X10008226. Am J Chin Med. 2010. PMID: 20626061
-
Protective role of polyphenols from Bauhinia hookeri against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepato- and nephrotoxicity in mice.Ren Fail. 2015 Aug;37(7):1198-207. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2015.1061886. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Ren Fail. 2015. PMID: 26382171
-
Hepatoprotective effects of methanol extract of Carissa opaca leaves on CCl4-induced damage in rat.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011 Jun 24;11:48. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-11-48. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011. PMID: 21699742 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Apoptosis Effects of Dihydrokaempferol Isolated from Bauhinia championii on Synoviocytes.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Dec 2;2018:9806160. doi: 10.1155/2018/9806160. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30622621 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Hepatoprotective activity of Eriocaulon quinquangulare in vitro using porcine liver slices against ethanol induced liver toxicity and free radical scavenging capacity.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Feb 24;16:74. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1044-x. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 26912176 Free PMC article.
-
Umbelliferone Ameliorates CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats by Upregulating PPARγ and Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and TGF-β1/Smad3 Signaling.Inflammation. 2019 Jun;42(3):1103-1116. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-00973-8. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 30741365
-
Chemical profile and biological activities of Lysiphyllum binatum (Blanco) de Wit.J Nat Med. 2025 Jan;79(1):45-58. doi: 10.1007/s11418-024-01844-9. Epub 2024 Sep 25. J Nat Med. 2025. PMID: 39320607
-
Hepatoprotective effects of blue honeysuckle on CCl4-induced acute liver damaged mice.Food Sci Nutr. 2018 Nov 27;7(1):322-338. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.893. eCollection 2019 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30680187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Setty SR, Quereshi AA, Swamy AHMV, et al. Hepatoprotective activity of Calotropis procera flowers against paracetamol-induced hepatic injury in rats. Fitoterapia. 2007;78(7-8):451–454. - PubMed
-
- Srivastava A, Shivanandappa T. Hepatoprotective effect of the root extract of Decalepis hamiltonii against carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative stress in rats. Food Chemistry. 2010;118(2):411–417.
-
- Williamson EM, Okpako DT, Evans FJ. Pharmacological Methods in Phytotherapy Research: Selection, Preparation and Pharmacological Evaluation of Plant Material. Vol. 1. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons; 1996.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

