Amygdala Atrophy in MCI/Alzheimer's Disease in the BIOCARD cohort based on Diffeomorphic Morphometry
- PMID: 24955432
- PMCID: PMC4063307
Amygdala Atrophy in MCI/Alzheimer's Disease in the BIOCARD cohort based on Diffeomorphic Morphometry
Abstract
Surface-based deformation markers obtained from diffeomorphic mapping of the amygdala are used to study specific atrophy patterns in a combined mild cognitively impaired and demented cohort compared with cognitively normal aging subjects. Statistical analysis demonstrates with high significance in a small sample of legacy data that deformation-based morphometry provides sensitive markers for locating atrophy in the amygdala. With respect to a high-field amygdala atlas, significant atrophy was found in the basomedial and lateral nucleus subregions.
Figures

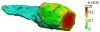

References
-
- Jernigan TL, et al. Cerebral Structure on Mri.2. Specific Changes in Alzheimers and Huntingtons Diseases. Biological Psychiatry. 1991;29(1):68–81. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82(4):239–59. - PubMed
-
- Arnold SE, et al. The topographical and neuroanatomical distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Cereb Cortex. 1991;1(1):103–16. - PubMed
-
- Price JL, Morris JC. Tangles and plaques in nondemented aging and “preclinical” Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol. 1999;45(3):358–68. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
