A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of selegiline transdermal system in depressed adolescents
- PMID: 24955812
- PMCID: PMC4137354
- DOI: 10.1089/cap.2013.0138
A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of selegiline transdermal system in depressed adolescents
Abstract
Objective: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled flexible-dose, parallel group trial was conducted at 26 clinical investigational sites in the United States to examine the safety and efficacy of the selegiline transdermal system (STS) (EMSAM®) in adolescents (ages 12-17 years) meeting American Psychiatric Association, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed. (DSM-IV) criteria for moderate to severe major depressive disorder (MDD) without psychotic features.
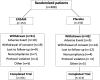
Methods: Adolescents (n=308) with moderate to severe MDD were randomized to either STS (n=152) or placebo (n=156). Two hundred and fifteen (69.8%) subjects completed the study and 17 (5.5%) reported discontinuation because of adverse events (AEs). The primary efficacy outcome measure was the mean change from baseline to end of study (week 12 last observation carried forward [LOCF]) in the Children's Depression Rating Scale-Revised (CDRS-R) total score. Secondary outcome measures included end-point Clinical Global Impressions - Severity (CGI-S) and Clinical Global Impressions - Improvement (CGI-I).
Results: Patients on STS or placebo had a significant decline from baseline (p<0.001) on their CDRS-R total score with mean reductions±SD as follows: STS 21.4±16.6; placebo 21.5±16.5. Both groups had similar response rates (58.6% vs. 59.3%) defined as CGI-I of 1 or 2 at study end. However, these between-group efficacy findings were without statistical significance. The overall incidence of reported AEs was 62.5% for STS-treated patients and 57.7% for placebo-treated patients. Most commonly reported AEs in STS or placebo groups were application site reactions (STS=24.3%; placebo=21.8%), headache (STS=17.1%; placebo=16.7%), and nausea (STS=7.2%; placebo=7.7%). Treatment groups did not differ on any laboratory parameters, vital signs, or electrocardiogram (ECG) findings. No suspected hypertensive crises were reported in the trial.
Conclusions: These data demonstrated that the STS was safe and well tolerated in this adolescent sample. However, both STS-treated and placebo-treated subjects demonstrated a decline from baseline in depressive symptoms (CDRS-R total score) over the length of the study, without statistical superiority by either group.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed., Text Revision. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000
-
- Amsterdam JD: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the safety and efficacy of selegiline transdermal system without dietary restrictions in patients with major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 64:208–214, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Amsterdam JD, Bodkin JA: Selegiline transdermal system in the prevention of relapse of major depressive disorder: A 52-week double-blind, placebo-substitution, parallel-group clinical trial. J Clin Psychopharmacol 26:579–586, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Azzaro AJ, VanDenBerg CM, Blob LF, Kemper EM, Sharoky M, Oren DA, Campbell BJ: Tyramine pressor sensitivity during treatment with selegiline transdermal system 6mg/24hrs in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 46:933–944, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Biederman J, Faraone S, Mick E, Lelon E: Psychiatric comorbidity among referred juveniles with major depression: Fact or artifact? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 34:579–590, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical