A meta-analysis and review of holistic face processing
- PMID: 24956123
- PMCID: PMC4152424
- DOI: 10.1037/a0037004
A meta-analysis and review of holistic face processing
Abstract
The concept of holistic processing is a cornerstone of face recognition research, yet central questions related to holistic processing remain unanswered, and debates have thus far failed to reach a resolution despite accumulating empirical evidence. We argue that a considerable source of confusion in this literature stems from a methodological problem. Specifically, 2 measures of holistic processing based on the composite paradigm (complete design and partial design) are used in the literature, but they often lead to qualitatively different results. First, we present a comprehensive review of the work that directly compares the 2 designs, and which clearly favors the complete design over the partial design. Second, we report a meta-analysis of holistic face processing according to both designs and use this as further evidence for one design over the other. The meta-analysis effect size of holistic processing in the complete design is nearly 3 times that of the partial design. Effect sizes were not correlated between measures, consistent with the suggestion that they do not measure the same thing. Our meta-analysis also examines the correlation between conditions in the complete design of the composite task, and suggests that in an individual differences context, little is gained by including a misaligned baseline. Finally, we offer a comprehensive review of the state of knowledge about holistic processing based on evidence gathered from the measure we favor based on the 1st sections of our review-the complete design-and outline outstanding research questions in that new context.
PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2014 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures


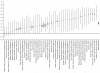
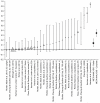


References
-
- Basso MR, Schefft BK, Ris MD, Dember WN. Mood and global-local visual processing. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society. 1996;2:249–255. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S1355617700001193. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Behrmann M, Marotta J, Gauthier I, Tarr MJ, McKeeff TJ. Behavioral change and its neural correlates in visual agnosia after expertise training. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2005;17(4):554–568. doi:10.1162/0898929053467613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

