5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl 5'-Monophosphate (AICAR), a Highly Conserved Purine Intermediate with Multiple Effects
- PMID: 24957512
- PMCID: PMC3901205
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo2020292
5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl 5'-Monophosphate (AICAR), a Highly Conserved Purine Intermediate with Multiple Effects
Abstract
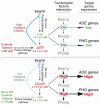
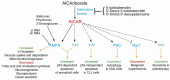
AICAR (5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl 5'-monophosphate) is a natural metabolic intermediate of purine biosynthesis that is present in all organisms. In yeast, AICAR plays important regulatory roles under physiological conditions, notably through its direct interactions with transcription factors. In humans, AICAR accumulates in several metabolic diseases, but its contribution to the symptoms has not yet been elucidated. Further, AICAR has highly promising properties which have been recently revealed. Indeed, it enhances endurance of sedentary mice. In addition, it has antiproliferative effects notably by specifically inducing apoptosis of aneuploid cells. Some of the effects of AICAR are due to its ability to stimulate the AMP-activated protein kinase but some others are not. It is consequently clear that AICAR affects multiple targets although only few of them have been identified so far. This review proposes an overview of the field and suggests future directions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Disruption of Nucleotide Homeostasis by the Antiproliferative Drug 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-d-ribofuranoside Monophosphate (AICAR).J Biol Chem. 2015 Sep 25;290(39):23947-59. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.656017. Epub 2015 Aug 17. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26283791 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of yeast and human 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-d-ribofuranoside (AICAr) transporters.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jun 13;289(24):16844-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.551192. Epub 2014 Apr 28. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24778186 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and toxic effects of purine intermediate 5-amino-4-imidazolecarboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) in yeast.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 2;286(35):30994-31002. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.262659. Epub 2011 Jul 12. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21757731 Free PMC article.
-
Dual effects of pyrazofurin and 3-deazauridine upon pyrimidine and purine biosynthesis in mouse L1210 leukemia.Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2645-50. Cancer Res. 1989. PMID: 2713848
-
Untargeted metabolomics confirms and extends the understanding of the impact of aminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide (AICAR) in the metabolic network of Salmonella enterica.Microb Cell. 2017 Nov 22;5(2):74-87. doi: 10.15698/mic2018.02.613. Microb Cell. 2017. PMID: 29417056 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Metabolomics and proteomics identify the toxic form and the associated cellular binding targets of the anti-proliferative drug AICAR.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jan 18;294(3):805-815. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004964. Epub 2018 Nov 26. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30478173 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed metabolic disturbances in the myocardium after exertional heat stroke: contrasting effects of exertion and thermal load.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2023 Nov 1;135(5):1186-1198. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00372.2023. Epub 2023 Oct 5. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2023. PMID: 37795530 Free PMC article.
-
Studying the Geroprotective Properties of YAP/TAZ Signaling Inhibitors on Drosophila melanogaster Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 22;24(6):6006. doi: 10.3390/ijms24066006. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36983079 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive Roles for AMPK and Glycogen from Cellular Energy Sensing to Exercise Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 26;19(11):3344. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113344. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30373152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of Nucleotide Homeostasis by the Antiproliferative Drug 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-d-ribofuranoside Monophosphate (AICAR).J Biol Chem. 2015 Sep 25;290(39):23947-59. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.656017. Epub 2015 Aug 17. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26283791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sabina R.L., Patterson D., Holmes E.W. 5-Amino-4-imidazolecarboxamide riboside (Z-riboside) metabolism in eukaryotic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1985;260:6107–6114. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

