Variability of CSF Alzheimer's disease biomarkers: implications for clinical practice
- PMID: 24959687
- PMCID: PMC4069102
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100784
Variability of CSF Alzheimer's disease biomarkers: implications for clinical practice
Abstract
Background: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers are increasingly being used for diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Objective: We investigated the influence of CSF intralaboratory and interlaboratory variability on diagnostic CSF-based AD classification of subjects and identified causes of this variation.
Methods: We measured CSF amyloid-β (Aβ) 1-42, total tau (t-tau), and phosphorylated tau (p-tau) by INNOTEST enzyme-linked-immunosorbent assays (ELISA) in a memory clinic population (n = 126). Samples were measured twice in a single or two laboratories that served as reference labs for CSF analyses in the Netherlands. Predefined cut-offs were used to classify CSF biomarkers as normal or abnormal/AD pattern.
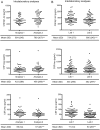
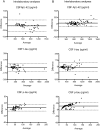
Results: CSF intralaboratory variability was higher for Aβ1-42 than for t-tau and p-tau. Reanalysis led to a change in biomarker classification (normal vs. abnormal) of 26% of the subjects based on Aβ1-42, 10% based on t-tau, and 29% based on p-tau. The changes in absolute biomarker concentrations were paralleled by a similar change in levels of internal control samples between different assay lots. CSF interlaboratory variability was higher for p-tau than for Aβ1-42 and t-tau, and reanalysis led to a change in biomarker classification of 12% of the subjects based on Aβ1-42, 1% based on t-tau, and 22% based on p-tau.
Conclusions: Intralaboratory and interlaboratory CSF variability frequently led to change in diagnostic CSF-based AD classification for Aβ1-42 and p-tau. Lot-to-lot variation was a major cause of intralaboratory variability. This will have implications for the use of these biomarkers in clinical practice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Blennow K, Hampel H (2003) CSF markers for incipient Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol 2: 605–613. - PubMed
-
- Vos SJB, van Rossum IA, Verhey F, Knol DL, Soininen H, et al. (2013) Prediction of Alzheimer’s disease in subjects with amnestic and non-amnestic MCI. Neurology 80: 1124–1132. - PubMed
-
- Lewczuk P, Beck G, Ganslandt O, Esselmann H, Deisenhammer F, et al. (2006) International quality control survey of neurochemical dementia diagnostics. Neurosci Lett 409: 1–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

