Multifunctional D2/D3 agonist D-520 with high in vivo efficacy: modulator of toxicity of alpha-synuclein aggregates
- PMID: 24960209
- PMCID: PMC4140597
- DOI: 10.1021/cn500084x
Multifunctional D2/D3 agonist D-520 with high in vivo efficacy: modulator of toxicity of alpha-synuclein aggregates
Abstract
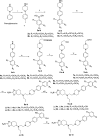
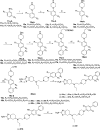
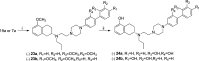
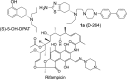
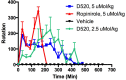
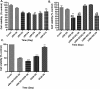
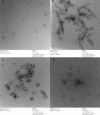
We have developed a series of dihydroxy compounds and related analogues based on our hybrid D2/D3 agonist molecular template to develop multifunctional drugs for symptomatic and neuroprotective treatment for Parkinson's disease (PD). The lead compound (-)-24b (D-520) exhibited high agonist potency at D2/D3 receptors and produced efficacious activity in the animal models for PD. The data from thioflavin T (ThT) assay and from transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis demonstrate that D-520 is able to modulate aggregation of alpha-synuclein (αSN). Additionally, coincubation of D-520 with αSN is able to reduce toxicity of preformed aggregates of αSN compared to control αSN alone. Finally, in a neuroprotection study with dopaminergic MN9D cells, D-520 clearly demonstrated the effect of neuroprotection from toxicity of 6-hydroxydopamine. Thus, compound D-520 possesses properties characteristic of multifunctionality conducive to symptomatic and neuroprotective treatment of PD.
Figures




References
-
- Braak H.; Del Tredici K.; Rub U.; de Vos R. A.; Jansen Steur E. N.; Braak E. (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 24, 197–211. - PubMed
-
- Paulus W.; Jellinger K. (1991) The neuropathologic basis of different clinical subgroups of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 50, 743–755. - PubMed
-
- Sherer T. B.; Betarbet R.; Greenamyre J. T. (2001) Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs 2, 657–662. - PubMed
-
- Fink A. L. (2006) The aggregation and fibrillation of alpha-synuclein. Acc. Chem. Res. 39, 628–634. - PubMed
-
- Berg D.; Gerlach M.; Youdim M. B.; Double K. L.; Zecca L.; Riederer P.; Becker G. (2001) Brain iron pathways and their relevance to Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 79, 225–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

