Cannabinoids: well-suited candidates for the treatment of perinatal brain injury
- PMID: 24961520
- PMCID: PMC4061885
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci3031043
Cannabinoids: well-suited candidates for the treatment of perinatal brain injury
Abstract
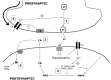
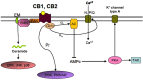
Perinatal brain injury can be induced by a number of different damaging events occurring during or shortly after birth, including neonatal asphyxia, neonatal hypoxia-ischemia and stroke-induced focal ischemia. Typical manifestations of these conditions are the presence of glutamate excitoxicity, neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, the combination of which can potentially result in apoptotic-necrotic cell death, generation of brain lesions and long-lasting functional impairment. In spite of the high incidence of perinatal brain injury, the number of clinical interventions available for the treatment of the affected newborn babies is extremely limited. Hence, there is a dramatic need to develop new effective therapies aimed to prevent acute brain damage and enhance the endogenous mechanisms of long-term brain repair. The endocannabinoid system is an endogenous neuromodulatory system involved in the control of multiple central and peripheral functions. An early responder to neuronal injury, the endocannabinoid system has been described as an endogenous neuroprotective system that once activated can prevent glutamate excitotoxicity, intracellular calcium accumulation, activation of cell death pathways, microglia activation, neurovascular reactivity and infiltration of circulating leukocytes across the blood-brain barrier. The modulation of the endocannabinoid system has proven to be an effective neuroprotective strategy to prevent and reduce neonatal brain injury in different animal models and species. Also, the beneficial role of the endocannabinoid system on the control of the endogenous repairing responses (neurogenesis and white matter restoration) to neonatal brain injury has been described in independent studies. This review addresses the particular effects of several drugs that modulate the activity of the endocannabinoid system on the progression of different manifestations of perinatal brain injury during both the acute and chronic recovery phases using rodent and non-rodent animal models, and will provide a complete description of the known mechanisms that mediate such effects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Therapeutic potential of the endocannabinoid system in perinatal asphyxia].Rev Neurol. 2011 Dec 16;53(12):758-64. Rev Neurol. 2011. PMID: 22127663 Review. Spanish.
-
The Long-Term Neuroprotective Effect of the Endocannabinoid 2-AG and Modulation of the SGZ's Neurogenic Response after Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 7;15(6):1667. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061667. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37376115 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid as a neuroprotective strategy in perinatal hypoxic-ischemic injury.Neurosci Bull. 2011 Aug;27(4):275-85. doi: 10.1007/s12264-011-1008-6. Neurosci Bull. 2011. PMID: 21788999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of integrating cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system in neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Apr 12;16:1152167. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1152167. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37122621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
Cited by
-
Perinatal asphyxia results in altered expression of the hippocampal acylethanolamide/endocannabinoid signaling system associated to memory impairments in postweaned rats.Front Neuroanat. 2015 Nov 3;9:141. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2015.00141. eCollection 2015. Front Neuroanat. 2015. PMID: 26578900 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabis, Cannabinoids, and Cerebral Metabolism: Potential Applications in Stroke and Disorders of the Central Nervous System.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2015 Sep;17(9):627. doi: 10.1007/s11886-015-0627-3. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26238742 Review.
-
Cannabinoids in Pediatrics.J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2017 May-Jun;22(3):176-185. doi: 10.5863/1551-6776-22.3.176. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28638299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabinoids in Neurodegenerative Disorders and Stroke/Brain Trauma: From Preclinical Models to Clinical Applications.Neurotherapeutics. 2015 Oct;12(4):793-806. doi: 10.1007/s13311-015-0381-7. Neurotherapeutics. 2015. PMID: 26260390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Antioxidants in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury: New Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 28;18(2):265. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020265. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28134843 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

