Insulin-induced localized lipoatrophy preceded by shingles (herpes zoster): a case report
- PMID: 24961832
- PMCID: PMC4086694
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-8-223
Insulin-induced localized lipoatrophy preceded by shingles (herpes zoster): a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Localized involutional lipoatrophy of subcutaneous adipose tissue may develop due to subcutaneous injection of pharmaceutical preparations. The pathogenesis of this adverse drug reaction is unknown. The progression of localized involutional lipoatrophy ceases and occasionally it resolves after withdrawing the inducing agent. In case of localized involutional lipoatrophy due to subcutaneous insulin therapy, low-dose systemic corticosteroids may be curative despite ongoing insulin administration.
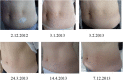
Case presentation: We report a recurrence of insulin-induced localized involutional lipoatrophy at the abdominal wall in a 57-year-old Caucasian woman with type-1 diabetes on continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. The first episode of insulin-induced localized involutional lipoatrophy two years previously had been cured by oral prednisone. The recurrence was treated immediately with 10mg prednisone once daily for five months, and was cured thereafter. The insulin analog preparation (Humalog™) and the insulin pump equipment (Accu-Chek Spirit™) applied were the same during both episodes. Both episodes were preceded by a temporary disturbance of the immune balance (the first episode by vaccination, the second episode through shingles).
Conclusions: This case confirms that insulin-induced localized involutional lipoatrophy in type-1 diabetes can occur again, and can be cured by systemic corticosteroids. We suggest that temporary disturbance of the immune balance may trigger this transitory idiosyncratic reaction in a susceptible individual.
Figures

References
-
- Lopez X, Castells M, Ricker A, Velazquez EF, Mun E, Goldfine AB. Human insulin analog-induced lipoatrophy. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:443–444. - PubMed
-
- Cabrera-Freitag P, Escalada J, Goikoetxea MJ, Laguna S, Sanz ML, Gastaminza G. A severe case of lipoatrophy due to human insulin and insulin analogs in a patient with diabetes: is an immunological mechanism involved? J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2011;21:417–419. - PubMed
-
- Aviles-Izquierdo JA, Longo-Imedio MI, Hernanz-Hermosa JM, Lazaro-Ochaita P. Bilateral localized lipoatrophy secondary to a single intramuscular corticosteroid injection. Dermatol Online J. 2006;12:17. - PubMed
-
- Peteiro-González D, Fernández-Rodríguez B, Cabezas-Agrícola JM, Araújo-Vilar D. Severe localized lipoatrophy related to therapy with insulin analogs in type 1a diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;91:e61–e63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

