The HIV Modes of Transmission model: a systematic review of its findings and adherence to guidelines
- PMID: 24962034
- PMCID: PMC4069382
- DOI: 10.7448/IAS.17.1.18928
The HIV Modes of Transmission model: a systematic review of its findings and adherence to guidelines
Abstract
Introduction: The HIV Modes of Transmission (MOT) model estimates the annual fraction of new HIV infections (FNI) acquired by different risk groups. It was designed to guide country-specific HIV prevention policies. To determine if the MOT produced context-specific recommendations, we analyzed MOT results by region and epidemic type, and explored the factors (e.g. data used to estimate parameter inputs, adherence to guidelines) influencing the differences.
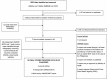
Methods: We systematically searched MEDLINE, EMBASE and UNAIDS reports, and contacted UNAIDS country directors for published MOT results from MOT inception (2003) to 25 September 2012.
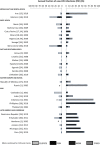
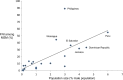
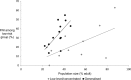
Results: We retrieved four journal articles and 20 UNAIDS reports covering 29 countries. In 13 countries, the largest FNI (range 26 to 63%) was acquired by the low-risk group and increased with low-risk population size. The FNI among female sex workers (FSWs) remained low (median 1.3%, range 0.04 to 14.4%), with little variability by region and epidemic type despite variability in sexual behaviour. In India and Thailand, where FSWs play an important role in transmission, the FNI among FSWs was 2 and 4%, respectively. In contrast, the FNI among men who have sex with men (MSM) varied across regions (range 0.1 to 89%) and increased with MSM population size. The FNI among people who inject drugs (PWID, range 0 to 82%) was largest in early-phase epidemics with low overall HIV prevalence. Most MOT studies were conducted and reported as per guidelines but data quality remains an issue.
Conclusions: Although countries are generally performing the MOT as per guidelines, there is little variation in the FNI (except among MSM and PWID) by region and epidemic type. Homogeneity in MOT FNI for FSWs, clients and low-risk groups may limit the utility of MOT for guiding country-specific interventions in heterosexual HIV epidemics.
Keywords: HIV; HIV infection; HIV prevention policy; Modes of Transmission model; epidemic appraisal; key populations.
Figures

References
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) Geneva: 2007. Modelling the expected short-term distribution of incidence of HIV infections by exposure group. [cited 2012 Sep 28]. Available from: http://www.unaids.org/en/dataanalysis/tools/incidencebymodesoftransmission.
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) Geneva: 2005. Intensifying HIV prevention: UNAIDS policy position paper. [cited 2013 Mar 15]. Available from: http://data.unaids.org/publications/irc-pub06/jc1165-intensif_hiv-newsty....
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), World Health Organization (WHO) Geneva: 2000. Second generation surveillance for HIV: the next decade. [cited 2013 Aug 15]. Available from: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/2000/WHO_CDS_CSR_EDC_2000.5.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

