Targeting TBK1 inhibits migration and resistance to MEK inhibitors in mutant NRAS melanoma
- PMID: 24962318
- PMCID: PMC4482471
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0204
Targeting TBK1 inhibits migration and resistance to MEK inhibitors in mutant NRAS melanoma
Abstract
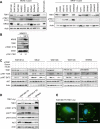
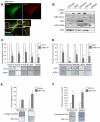
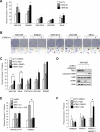
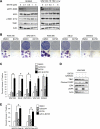
Melanoma is a devastating form of skin cancer with limited therapeutic options. Fifteen to 20% of patients with melanoma have an activating mutation in the GTPase, NRAS. The major downstream effectors of RAS are RAFs (ARAF, BRAF, and CRAF), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and the Ral guanine exchange factors (RalGEF). TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) is an atypical IκB kinase family member that acts downstream of RalGEFs. Whereas many studies have analyzed RAF and PI3K signaling in mutant NRAS melanoma, the role of RalGEF/Ral is understudied and TBK1 has not been examined. To address this, TBK1 was modulated with knockdown approaches and targeted therapies to determine the role of TBK1 in motility, apoptosis, and signaling. In melanoma, NRAS overexpression increased TBK1 phosphorylation. TBK1 depletion inhibited migration and invasion, whereas its constitutive overexpression led to an increase in invasion. In three-dimensional systems that mimic the dermal microenvironment, TBK1 depletion or inhibition cooperated with MEK inhibitors to promote apoptosis, particularly in the context of MEK-insensitive mutant NRAS. This effect was absent in melanoma cells that are wild-type for NRAS. These results suggest the utility of TBK1 inhibitors as part of a treatment regimen for patients with mutant NRAS melanoma, for whom there are no current effective therapies.
Implications: TBK1 promotes the malignant properties of NRAS-mutant melanoma and its targeting, in combination with MEK, promotes apoptosis, thus providing a potential novel targeted therapeutic option.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficient Suppression of NRAS-Driven Melanoma by Co-Inhibition of ERK1/2 and ERK5 MAPK Pathways.J Invest Dermatol. 2020 Dec;140(12):2455-2465.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2020.03.972. Epub 2020 May 4. J Invest Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32376279
-
P53 and MITF/Bcl-2 identified as key pathways in the acquired resistance of NRAS-mutant melanoma to MEK inhibition.Eur J Cancer. 2017 Sep;83:154-165. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.06.033. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Eur J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28738256
-
Combined targeting of MEK and PI3K/mTOR effector pathways is necessary to effectively inhibit NRAS mutant melanoma in vitro and in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Mar 5;110(10):4015-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216013110. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23431193 Free PMC article.
-
MEK inhibitors for the treatment of NRAS mutant melanoma.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Aug 20;12:2553-2565. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S131721. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30154648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Binimetinib for the treatment of NRAS-mutant melanoma.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2017 Nov;17(11):985-990. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2017.1374177. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28851243 Review.
Cited by
-
The Specific IKKε/TBK1 Inhibitor Amlexanox Suppresses Human Melanoma by the Inhibition of Autophagy, NF-κB and MAP Kinase Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 2;21(13):4721. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134721. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32630674 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of TBK1/IKKε Promotes Regeneration of Pancreatic β-cells.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 22;8(1):15587. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33875-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30349097 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Methylation Module Network-Based Prognosis and Molecular Typing of Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2019 Jul 28;10(8):571. doi: 10.3390/genes10080571. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31357729 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient prioritization of CRISPR screen hits by accounting for targeting efficiency of guide RNA.BMC Biol. 2023 Feb 24;21(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12915-023-01536-y. BMC Biol. 2023. PMID: 36829149 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting PHGDH Upregulation Reduces Glutathione Levels and Resensitizes Resistant NRAS-Mutant Melanoma to MAPK Kinase Inhibition.J Invest Dermatol. 2020 Nov;140(11):2242-2252.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2020.02.047. Epub 2020 May 7. J Invest Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32389536 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howe HL, Wu X, Ries LA, Cokkinides V, Ahmed F, Jemal A, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975-2003, featuring cancer among U.S. Hispanic/Latino populations. Cancer. 2006;107:1711–42. - PubMed
-
- Miller AJ, Mihm MC., Jr. Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:51–65. - PubMed
-
- Russo AE, Torrisi E, Bevelacqua Y, Perrotta R, Libra M, McCubrey JA, et al. Melanoma: molecular pathogenesis and emerging target therapies (Review). Int J Oncol. 2009;34:1481–9. - PubMed
-
- Soengas MS, Lowe SW. Apoptosis and melanoma chemoresistance. Oncogene. 2003;22:3138–51. - PubMed
-
- Gray-Schopfer V, Wellbrock C, Marais R. Melanoma biology and new targeted therapy. Nature. 2007;445:851–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

