Genome-wide survival analysis of age at onset of alcohol dependence in extended high-risk COGA families
- PMID: 24962325
- PMCID: PMC4127128
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.05.023
Genome-wide survival analysis of age at onset of alcohol dependence in extended high-risk COGA families
Abstract
Background: The age at onset of alcohol dependence (AD) is a critical moderator of genetic associations for alcohol dependence. The present study evaluated whether single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can influence the age at onset of AD in large high-risk families from the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA).
Methods: Genomewide SNP genotyping was performed in 1788 regular drinkers from 118 large European American families densely affected with alcoholism. We used a genome-wide Cox proportional hazards regression model to test for association between age at onset of AD and SNPs.
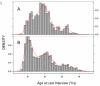
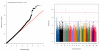
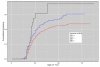
Results: This family-based analysis identified an intergenic SNP, rs2168784 on chromosome 3 that showed strong evidence of association (P=5×10(-9)) with age at onset of AD among regular drinkers. Carriers of the minor allele of rs2168784 had 1.5 times the hazard of AD onset as compared with those homozygous for the major allele. By the age of 20 years, nearly 30% of subjects homozygous for the minor allele were alcohol dependent while only 19% of those homozygous for the major allele were. We also identified intronic SNPs in the ADP-ribosylation factor like 15 (ARL15) gene on chromosome 5 (P=1.11×10(-8)) and the UTP20 small subunit (UTP20) gene on chromosome 12 (P=4.32×10(-8)) that were associated with age at onset of AD.
Conclusions: This extended family based genome-wide cox-proportional hazards analysis identified several loci that might be associated with age at onset of AD.
Keywords: Age at onset; Alcohol dependence; GWAS; SNP; Survival analysis.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A meta-analysis of two genome-wide association studies to identify novel loci for maximum number of alcoholic drinks.Hum Genet. 2013 Oct;132(10):1141-51. doi: 10.1007/s00439-013-1318-z. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23743675 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide polygenic scores for age at onset of alcohol dependence and association with alcohol-related measures.Transl Psychiatry. 2016 Mar 22;6(3):e761. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.27. Transl Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27003187 Free PMC article.
-
Common variants in HLA-DRA gene are associated with alcohol dependence in two Caucasian samples.J Mol Neurosci. 2013 Mar;49(3):574-81. doi: 10.1007/s12031-012-9869-3. Epub 2012 Aug 14. J Mol Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 22890421
-
Alcohol Dependence Genetics: Lessons Learned From Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) and Post-GWAS Analyses.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015 Aug;39(8):1312-27. doi: 10.1111/acer.12792. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015. PMID: 26110981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The collaborative study on the genetics of alcoholism: Genetics.Genes Brain Behav. 2023 Oct;22(5):e12856. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12856. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Genes Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 37387240 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic determinants of beverage consumption: Implications for nutrition and health.Adv Food Nutr Res. 2019;89:1-52. doi: 10.1016/bs.afnr.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Apr 19. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2019. PMID: 31351524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study of Dietary Pattern Scores.Nutrients. 2017 Jun 23;9(7):649. doi: 10.3390/nu9070649. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28644415 Free PMC article.
-
Using an Event-History with Risk-Free Model to Study the Genetics of Alcoholism.Sci Rep. 2017 May 16;7(1):1975. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01791-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28512340 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Environmental Interplay in Adolescent Substance Use Disorders.Curr Addict Rep. 2015 Jun;2(2):122-129. doi: 10.1007/s40429-015-0049-8. Curr Addict Rep. 2015. PMID: 26301173 Free PMC article.
-
A Whole Methylome Study of Ethanol Exposure in Brain and Blood: An Exploration of the Utility of Peripheral Blood as Proxy Tissue for Brain in Alcohol Methylation Studies.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2018 Dec;42(12):2360-2368. doi: 10.1111/acer.13905. Epub 2018 Nov 11. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2018. PMID: 30320886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baik I, Cho NH, Kim SH, Han BG, Shin C. Genome-wide association studies identify genetic loci related to alcohol consumption in Korean men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011;93:809–816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

