The C-terminal domain of the DNA polymerase catalytic subunit regulates the primase and polymerase activities of the human DNA polymerase α-primase complex
- PMID: 24962573
- PMCID: PMC4139218
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.570333
The C-terminal domain of the DNA polymerase catalytic subunit regulates the primase and polymerase activities of the human DNA polymerase α-primase complex
Abstract
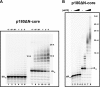
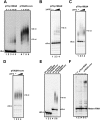
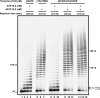
The initiation of DNA synthesis during replication of the human genome is accomplished primarily by the DNA polymerase α-primase complex, which makes the RNA-DNA primers accessible to processive DNA pols. The structural information needed to understand the mechanism of regulation of this complex biochemical reaction is incomplete. The presence of two enzymes in one complex poses the question of how these two enzymes cooperate during priming of DNA synthesis. Yeast two-hybrid and direct pulldown assays revealed that the N-terminal domain of the large subunit of primase (p58N) directly interacts with the C-terminal domain of the catalytic subunit of polα (p180C). We found that a complex of the C-terminal domain of the catalytic subunit of polα with the second subunit (p180C-p70) stimulated primase activity, whereas the whole catalytically active heterodimer of polα (p180ΔN-p70) inhibited RNA synthesis by primase. Conversely, the polα catalytic domain without the C-terminal part (p180ΔN-core) possessed a much higher propensity to extend the RNA primer than the two-subunit polα (p180ΔN-p70), suggesting that p180C and/or p70 are involved in the negative regulation of DNA pol activity. We conclude that the interaction between p180C, p70, and p58 regulates the proper primase and polymerase function. The composition of the template DNA is another important factor determining the activity of the complex. We have found that polα activity strongly depends on the sequence of the template and that homopyrimidine runs create a strong barrier for DNA synthesis by polα.
Keywords: C-terminal Domain; DNA Polymerase; DNA Polymerase Activity; DNA Polymerase α-Primase; DNA Primase; DNA Replication; DNA Replication Initiation; Primase Activity; Protein-Protein Interaction; RNA.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Garg P., Burgers P. M. (2005) DNA polymerases that propagate the eukaryotic DNA replication fork. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 40, 115–128 - PubMed
-
- Pavlov Y. I., Shcherbakova P. V., Rogozin I. B. (2006) Roles of DNA polymerases in replication, repair, and recombination in eukaryotes. Int. Rev. Cytol. 255, 41–132 - PubMed
-
- MacNeill S. (2012) Composition and dynamics of the eukaryotic replisome: a brief overview. Subcell. Biochem. 62, 1–17 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

