The Kto-Skd complex can regulate ptc expression by interacting with Cubitus interruptus (Ci) in the Hedgehog signaling pathway
- PMID: 24962581
- PMCID: PMC4139242
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.560995
The Kto-Skd complex can regulate ptc expression by interacting with Cubitus interruptus (Ci) in the Hedgehog signaling pathway
Abstract
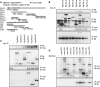
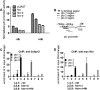
The hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway plays a very important role in metazoan development by controlling pattern formation. Drosophila imaginal discs are subdivided into anterior and posterior compartments that derive from adjacent cell populations. The anterior/posterior (A/P) boundaries, which are critical to maintaining the position of organizers, are established by a complex mechanism involving Hh signaling. Here, we uncover the regulation of ptc in the Hh signaling pathway by two subunits of mediator complex, Kto and Skd, which can also regulate boundary location. Collectively, we provide further evidence that Kto-Skd affects the A/P-axial development of the whole wing disc. Kto can interact with Cubitus interruptus (Ci), bind to the Ci-binding region on ptc promoter, which are both regulated by Hh signals to down-regulate ptc expression.
Keywords: Development; Drosophila; Hedgehog Signaling Pathway; Signal Transduction; Transcription.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hyperplastic discs differentially regulates the transcriptional outputs of hedgehog signaling.Mech Dev. 2014 Aug;133:117-25. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2014.05.002. Epub 2014 May 20. Mech Dev. 2014. PMID: 24854243 Free PMC article.
-
An absolute requirement for Cubitus interruptus in Hedgehog signaling.Development. 2001 Mar;128(5):733-42. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.5.733. Development. 2001. PMID: 11171398
-
In vivo RNAi screen reveals neddylation genes as novel regulators of Hedgehog signaling.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24168. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024168. Epub 2011 Sep 8. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21931660 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog signaling and the axial patterning of Drosophila wings.Biochem Cell Biol. 2000;78(5):585-91. doi: 10.1139/o00-072. Biochem Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11103949 Review.
-
Decoding Ci: from partial degradation to inhibition.Dev Growth Differ. 2015 Feb;57(2):98-108. doi: 10.1111/dgd.12187. Epub 2014 Dec 14. Dev Growth Differ. 2015. PMID: 25495033 Review.
Cited by
-
Controlling the Master: Chromatin Dynamics at the MYC Promoter Integrate Developmental Signaling.Genes (Basel). 2017 Apr 11;8(4):118. doi: 10.3390/genes8040118. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28398229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UbcD1 regulates Hedgehog signaling by directly modulating Ci ubiquitination and processing.EMBO Rep. 2017 Nov;18(11):1922-1934. doi: 10.15252/embr.201643289. Epub 2017 Sep 8. EMBO Rep. 2017. PMID: 28887318 Free PMC article.
-
Tetramethylpyrazine Inhibits Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells through Hedgehog Signaling Pathways In Vitro.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:603067. doi: 10.1155/2015/603067. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26380286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ingham P. W., McMahon A. P. (2001) Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 15, 3059–3087 - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Bellido A., Ripoll P., Morata G. (1973) Developmental compartmentalisation of the wing disk of Drosophila. Nature: New Biology 245, 251–253 - PubMed
-
- Lee J. J., von Kessler D. P., Parks S., Beachy P. A. (1992) Secretion and localized transcription suggest a role in positional signaling for products of the segmentation gene hedgehog. Cell 71, 33–50 - PubMed
-
- Tabata T., Kornberg T. B. (1994) Hedgehog is a signaling protein with a key role in patterning Drosophila imaginal discs. Cell 76, 89–102 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

