Chemical proteomics identifies heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) A1 as the molecular target of quercetin in its anti-cancer effects in PC-3 cells
- PMID: 24962584
- PMCID: PMC4139222
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.553248
Chemical proteomics identifies heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) A1 as the molecular target of quercetin in its anti-cancer effects in PC-3 cells
Abstract
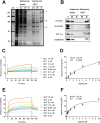
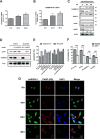
Quercetin, a flavonoid abundantly present in plants, is widely used as a phytotherapy in prostatitis and prostate cancer. Although quercetin has been reported to have a number of therapeutic effects, the cellular target(s) responsible for its anti-cancer action has not yet been clearly elucidated. Here, employing affinity chromatography and mass spectrometry, we identified heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNPA1) as a direct target of quercetin. A specific interaction between quercetin and hnRNPA1 was validated by immunoblotting and in vitro binding experiments. We found that quercetin bound the C-terminal region of hnRNPA1, impairing the ability of hnRNPA1 to shuttle between the nucleus and cytoplasm and ultimately resulting in its cytoplasmic retention. In addition, hnRNPA1 was recruited to stress granules after treatment of cells with quercetin for up to 48 h, and the levels of cIAP1 (cellular inhibitor of apoptosis), an internal ribosome entry site translation-dependent protein, were reduced by hnRNPA1 regulation. This is the first report that anti-cancer effects of quercetin are mediated, in part, by impairing functions of hnRNPA1, insights that were obtained using a chemical proteomics strategy.
Keywords: Chemical Proteomics; Molecular Target; Natural Product; Prostate Cancer; Protein Targeting; Proteomics; Quercetin; RNA-binding Protein; hnRNPA1.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
NF-κB2/p52:c-Myc:hnRNPA1 Pathway Regulates Expression of Androgen Receptor Splice Variants and Enzalutamide Sensitivity in Prostate Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Aug;14(8):1884-95. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-1057. Epub 2015 Jun 8. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 26056150 Free PMC article.
-
Subcellular relocalization of a trans-acting factor regulates XIAP IRES-dependent translation.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Apr;18(4):1302-11. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-06-0515. Epub 2007 Feb 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17287399 Free PMC article.
-
ALS-linked mutations in ubiquilin-2 or hnRNPA1 reduce interaction between ubiquilin-2 and hnRNPA1.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 May 1;24(9):2565-77. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv020. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 25616961
-
Clinical heterogeneity in a family with flail arm syndrome and review of hnRNPA1-related spectrum.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2022 Dec;9(12):1910-1917. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51682. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36314424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 in health and neurodegenerative disease: from structural insights to post-transcriptional regulatory roles.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013 Sep;56:436-46. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2012.12.002. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23247072 Review.
Cited by
-
H3.3-G34W in giant cell tumor of bone functionally aligns with the exon choice repressor hnRNPA1L2.Cancer Gene Ther. 2024 Aug;31(8):1177-1185. doi: 10.1038/s41417-024-00776-6. Epub 2024 May 29. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 38811797 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of mammary tumor cells can be induced by shikonin via direct binding-interference with hnRNPA1.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 12;7(28):43629-43653. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9660. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27248319 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B: an emerging group of cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Jul 25;8(1):337. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01129-8. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35879279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repurposing Potential of Riluzole as an ITAF Inhibitor in mTOR Therapy Resistant Glioblastoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 5;21(1):344. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010344. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31948038 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulatory Network of hnRNPs Underlying Regulating PKM Alternative Splicing in Tumor Progression.Biomolecules. 2024 May 9;14(5):566. doi: 10.3390/biom14050566. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38785973 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Murphy A. B., Macejko A., Taylor A., Nadler R. B. (2009) Chronic prostatitis: management strategies. Drugs 69, 71–84 - PubMed
-
- Vijayababu M. R., Kanagaraj P., Arunkumar A., Ilangovan R., Aruldhas M. M., Arunakaran J. (2005) Quercetin-induced growth inhibition and cell death in prostatic carcinoma cells (PC-3) are associated with increase in p21 and hypophosphorylated retinoblastoma proteins expression. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 131, 765–771 - PubMed
-
- Kumar R., Verma V., Jain A., Jain R. K., Maikhuri J. P., Gupta G. (2011) Synergistic chemoprotective mechanisms of dietary phytoestrogens in a select combination against prostate cancer. J. Nutr. Biochem. 22, 723–731 - PubMed
-
- Lamson D. W., Brignall M. S. (2000) Antioxidants and cancer, part 3: quercetin. Altern. Med. Rev. 5, 196–208 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Research Materials

