CarD integrates three functional modules to promote efficient transcription, antibiotic tolerance, and pathogenesis in mycobacteria
- PMID: 24962732
- PMCID: PMC4127138
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.12681
CarD integrates three functional modules to promote efficient transcription, antibiotic tolerance, and pathogenesis in mycobacteria
Abstract
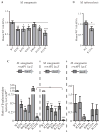
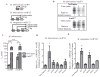
Although the basic mechanisms of prokaryotic transcription are conserved, it has become evident that some bacteria require additional factors to allow for efficient gene transcription. CarD is an RNA polymerase (RNAP)-binding protein conserved in numerous bacterial species and essential in mycobacteria. Despite the importance of CarD, its function at transcription complexes remains unclear. We have generated a panel of mutations that individually target three independent functional modules of CarD: the RNAP interaction domain, the DNA-binding domain, and a conserved tryptophan residue. We have dissected the roles of each functional module in CarD activity and built a model where each module contributes to stabilizing RNAP-promoter complexes. Our work highlights the requirement of all three modules of CarD in the obligate pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but not in Mycobacterium smegmatis. We also report divergent use of the CarD functional modules in resisting oxidative stress and pigmentation. These studies provide new information regarding the functional domains involved in transcriptional regulation by CarD while also improving understanding of the physiology of M. tuberculosis.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of Increasing the Affinity of CarD for RNA Polymerase on Mycobacterium tuberculosis Growth, rRNA Transcription, and Virulence.J Bacteriol. 2017 Jan 30;199(4):e00698-16. doi: 10.1128/JB.00698-16. Print 2017 Feb 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 27920294 Free PMC article.
-
Domains within RbpA Serve Specific Functional Roles That Regulate the Expression of Distinct Mycobacterial Gene Subsets.J Bacteriol. 2018 Jun 11;200(13):e00690-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00690-17. Print 2018 Jul 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29686140 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of CarD, an essential mycobacterial transcription factor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jul 30;110(31):12619-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1308270110. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23858468 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory action of the myxobacterial CarD/CarG complex: a bacterial enhanceosome?FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010 Sep;34(5):764-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00235.x. Epub 2010 May 20. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20561058 Review.
-
House of CarDs: Functional insights into the transcriptional regulator CdnL.Mol Microbiol. 2024 Nov;122(5):789-796. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15268. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Mol Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38664995 Review.
Cited by
-
Early diagnosis and effective treatment regimens are the keys to tackle antimicrobial resistance in tuberculosis (TB): A report from Euroscicon's international TB Summit 2016.Virulence. 2017 Aug 18;8(6):1005-1024. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1256536. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Virulence. 2017. PMID: 27813702 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the Tolfenamic Acid Binding Pocket in PrbP from Liberibacter asiaticus.Front Microbiol. 2017 Aug 23;8:1591. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01591. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28878750 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Steady State Ribosomal Transcription in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Intersection of Sigma Subunits, Superhelicity, and Transcription Factors.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 27:2025.02.24.639987. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.24.639987. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Biol Chem. 2025 Jun 12;301(8):110369. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110369. PMID: 40060575 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Effects of Increasing the Affinity of CarD for RNA Polymerase on Mycobacterium tuberculosis Growth, rRNA Transcription, and Virulence.J Bacteriol. 2017 Jan 30;199(4):e00698-16. doi: 10.1128/JB.00698-16. Print 2017 Feb 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 27920294 Free PMC article.
-
Redox Brake Regulator RedB and FnrL Function as Yin-Yang Regulators of Anaerobic-Aerobic Metabolism in Rhodobacter capsulatus.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0235422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02354-22. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36106752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bremer H, Dennis PP. Escherichia Coli and Salmonella Typhimurium: Cellular and Molecular Biology. ASM Press; 1996. Modulation of Chemical Composition and Other Parameters of the Cell by Growth Rate; pp. 1553–69.
-
- Chao MC, Rubin EJ. Letting sleeping dos lie: does dormancy play a role in tuberculosis? Annu Rev Microbiol. 2010;64:293–311. - PubMed
-
- Gaal T, Ross W, Estrem ST, Nguyen LH, Burgess RR, Gourse RL. Promoter recognition and discrimination by EsigmaS RNA polymerase. Mol Microbiol. 2001;42:939–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

