Apelin promotes lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis
- PMID: 24962866
- PMCID: PMC4147335
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2032
Apelin promotes lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis
Abstract
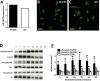
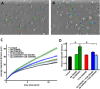
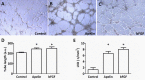
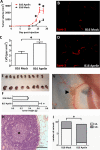
Whereas the role of the G-protein-coupled APJ receptor and its ligand, apelin, in angiogenesis has been well documented, the ability of the apelin/APJ system to induce lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis has been largely unexplored. To this end, we first show that APJ is expressed in lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) and, moreover, that it responds to apelin by activating the apelinergic signaling cascade. We find that although apelin treatment does not influence the proliferation of LECs in vitro, it enhances their migration, protects them against UV irradiation-induced apoptosis, increases their spheroid numbers in 3D culture, stimulates their in vitro capillary-like tube formation and, furthermore, promotes the invasive growth of lymphatic microvessels in vivo in the matrigel plug assay. We also demonstrate that apelin overexpression in malignant cells is associated with accelerated in vivo tumor growth and with increased intratumoral lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis. These results indicate that apelin induces lymphangiogenesis and, accordingly, plays an important role in lymphatic tumor progression. Our study does not only reveal apelin as a novel lymphangiogenic factor but might also open the door for the development of novel anticancer therapies targeting lymphangiogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Karpanen T, Alitalo K. Molecular biology and pathology of lymphangiogenesis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2008;3:367–397. - PubMed
-
- Stacker SA, Williams SP, Karnezis T, Shayan R, Fox SB, Achen MG. Lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic vessel remodelling in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14(3):159–172. - PubMed
-
- Pitkin SL, Maguire JJ, Bonner TI, Davenport AP. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXIV. Apelin receptor nomenclature, distribution, pharmacology, and function. Pharmacol Rev. 2010;62(3):331–342. - PubMed
-
- Devic E, Rizzoti K, Bodin S, Knibiehler B, Audigier Y. Amino acid sequence and embryonic expression of msr/apj, the mouse homolog of Xenopus X-msr and human APJ. Mech Dev. 1999;84(1-2):199–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

