Dexmedetomidine ameliorates monitored anaesthesia care
- PMID: 24963179
- PMCID: PMC4050931
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5049.130816
Dexmedetomidine ameliorates monitored anaesthesia care
Abstract
Background and aims: Monitored anaesthesia care (MAC) is meant for procedures under local anaesthesia. Various drugs have been used for this purpose. The recently introduced alpha2 agonist, dexmedetomidine provides "conscious sedation" with adequate analgesia and minimal respiratory depression. Hence, the safety and efficacy of two doses of dexmedetomidine for sedation and analgesia were evaluated.
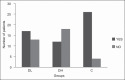
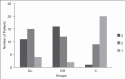
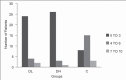
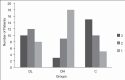
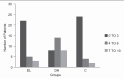
Methods: A total of 90 patients were distributed in three groups of 30 each: Dexmedetomidine 0.5 μg/kg (DL), dexmedetomidine 1.0 μg/kg (DH) and normal saline (C). The initial loading dose was followed by maintenance infusion of 0.2-0.7 μg/kg/h of dexmedetomidine or equivalent volume of saline. Study drug was started at least 15 min before placement of local anaesthesia. Drugs were titrated to a target level of sedation (=3 on Ramsay sedation scale [RSS]). Midazolam 0.02 mg/kg for RSS < 3 and fentanyl 0.5 μg/kg were supplemented as required. The statistical analysis was performed using Chi-square test and mean and anova analysis.
Results: In groups DL and DH fewer patients required supplemental midazolam, 56.7% (17/30) and 40% (12/30), compared with control, where 86.7% (26/30)needed midazolam supplements. P = 0.000. Both groups DL and DH required significantly less fentanyl (84.8 and 83.9 μg) versus control (144.2 μg). There was significantly increased ease of achieving and maintaining targeted sedation and analgesia in both dexmedetomidine groups when compared with placebo (P = 0.001). Adverse events observed with dexmedetomidine were bradycardia and hypotension.
Conclusions: Dexmedetomidine in the doses studied was considered safe and effective sedative and analgesic for patients undergoing procedures under MAC.
Keywords: Conscious sedation; dexmedetomidine; monitored anaesthesia care; respiratory depression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Rego M, White PF. Monitored anesthesia care. In: Miller RD, editor. Textbook of Ansthesiology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone; 2000. pp. 1452–67.
-
- Janzen PR, Christys A, Vucevic M. Patient-controlled sedation using propofol in elderly patients in day-case cataract surgery. Br J Anaesth. 1999;82:635–6. - PubMed
-
- Alhashemi JA. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for monitored anaesthesia care during cataract surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2006;96:722–6. - PubMed
-
- Scholz J, Tonner PH. Alpha2-adrenoceptor agonists in anaesthesia: A new paradigm. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2000;13:437–42. - PubMed
-
- Kamibayashi T, Maze M. Clinical uses of alpha2-adrenergic agonists. Anesthesiology. 2000;93:1345–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources