Household food insecurity: a systematic review of the measuring instruments used in epidemiological studies
- PMID: 24963759
- PMCID: PMC10271489
- DOI: 10.1017/S1368980014001050
Household food insecurity: a systematic review of the measuring instruments used in epidemiological studies
Abstract
Objective: To conduct a systematic review aimed at identifying and characterizing the experience-based household food security scales and to synthesize their psychometric properties.
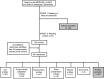
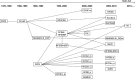
Design: Search in the MEDLINE, LILACS and SciELO databases, using the descriptors ('food insecurity' OR 'food security') AND ('questionnaires' OR 'scales' OR 'validity' OR 'reliability'). There was no limitation on the period of publication. All articles had their titles and abstracts analysed by two reviewers. The studies of interest were read in their entirety and the relevant information extracted using a standard form.
Results: The initial bibliographic search identified 299 articles. Of these, the 159 that seemed to meet the criteria for inclusion were read fully. After consultation of the bibliographic references of these articles, twenty articles and five documents were added, as they satisfied the previously determined criteria for inclusion. Twenty-four different instruments were identified; all were brief and of easy application. The majority were devised in the USA. Forty-seven references reported results of psychometric studies. The instruments that presented the highest number of psychometric studies were the Core Food Security Measurement/Household Food Security Survey Module (CFSM/HFSSM) and the Self-Perceived Household Food Security Scale.
Conclusions: There are a number of structured scales available in the literature for characterization of household food insecurity. However, despite some psychometric studies already existing about the majority of the instruments, it is observed that, except for the studies of the CFSM/HFSSM, these are still restricted to appraisal of a few aspects of reliability and validity.
Keywords: Systematic review.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (2000) Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). http://www.who.int/topics/millennium_development_goals/about/en/index.html (accessed September 2010).
-
- Bickel G, Nord M, Price C et al.. (2000) Guide to Measuring Household Food Security – Revised 2000. Alexandria, VA: USDA/Food and Nutrition Service.
-
- Kepple AW & Segall-Corrêa AM (2011) Conceituando e medindo segurança alimentar e nutricional. Cienc Saude Coletiva 16, 187–199. - PubMed
-
- Coates J (2013) Build it back better: deconstructing food security for improved measurement and action. Glob Food Sec 2, 188–194.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

