Heterogeneous computing architecture for fast detection of SNP-SNP interactions
- PMID: 24964802
- PMCID: PMC4230497
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-216
Heterogeneous computing architecture for fast detection of SNP-SNP interactions
Abstract
Background: The extent of data in a typical genome-wide association study (GWAS) poses considerable computational challenges to software tools for gene-gene interaction discovery. Exhaustive evaluation of all interactions among hundreds of thousands to millions of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) may require weeks or even months of computation. Massively parallel hardware within a modern Graphic Processing Unit (GPU) and Many Integrated Core (MIC) coprocessors can shorten the run time considerably. While the utility of GPU-based implementations in bioinformatics has been well studied, MIC architecture has been introduced only recently and may provide a number of comparative advantages that have yet to be explored and tested.
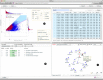
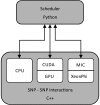
Results: We have developed a heterogeneous, GPU and Intel MIC-accelerated software module for SNP-SNP interaction discovery to replace the previously single-threaded computational core in the interactive web-based data exploration program SNPsyn. We report on differences between these two modern massively parallel architectures and their software environments. Their utility resulted in an order of magnitude shorter execution times when compared to the single-threaded CPU implementation. GPU implementation on a single Nvidia Tesla K20 runs twice as fast as that for the MIC architecture-based Xeon Phi P5110 coprocessor, but also requires considerably more programming effort.
Conclusions: General purpose GPUs are a mature platform with large amounts of computing power capable of tackling inherently parallel problems, but can prove demanding for the programmer. On the other hand the new MIC architecture, albeit lacking in performance reduces the programming effort and makes it up with a more general architecture suitable for a wider range of problems.
Figures


References
-
- Owens JD, Houston M, Luebke D, Green S, Stone JE, Phillips JC. Proceedings of the IEEE. New York, USA: IEEE; 2008. GPU computing; pp. 879–899.
-
- Nickolls J, Dally WJ. The GPU computing era. IEEE Micro. 2010;30(2):56–69.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

