Automated versus manual hippocampal segmentation in preoperative and postoperative patients with epilepsy
- PMID: 24965103
- PMCID: PMC4167188
- DOI: 10.1111/epi.12694
Automated versus manual hippocampal segmentation in preoperative and postoperative patients with epilepsy
Abstract
Objective: To compare manual and automated preoperative and postoperative hippocampal volume measurements in patients with intractable epilepsy.
Methods: We studied 34 patients referred to the Clinical Epilepsy Section, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), National Institutes of Health (NIH) for evaluation of intractable epilepsy and 21 normal volunteers who received 1.5 or 3 T GE Signa magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. Hippocampal volumes were traced manually on each slice and assembled into three-dimensional volumes by investigators who were blinded to other data. Automated volumetric measurements were obtained using FreeSurfer. Statistical analysis was performed with GraphPad Prism.
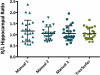
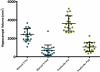
Results: Automated hippocampal volumes were larger than manual volumes in both patients and normal volunteers (p < 0.05). Right to left hemisphere hippocampal ratio and percent of hippocampus resected did not differ significantly by segmentation method. It was not possible to obtain accurate total resection volumes with the automated method.
Significance: Values such as side-to-side ratio and percent resected may be more directly translatable between manual and automated methods than absolute measures of volume. Accurate determination of resection volumes is important for studies of the effects of surgery on both seizure control and postoperative neuropsychological deficits. Our preliminary data suggest that FreeSurfer may provide an accurate and simple method for quantitating hippocampal resections. However, it may be less valuable for large or extratemporal resections, or when distortions of normal anatomy are present. A PowerPoint slide summarizing this article is available for download in the Supporting Information section here.
Keywords: Epilepsy; Hippocampus; Magnetic resonance imaging; Segmentation.
Published 2014. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures


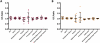
References
-
- Kim H, Chupin M, Colliot O, et al. Automatic hippocampal segmentation in temporal lobe epilepsy: Impact of developmental abnormalities. NeuroImage. 2012;59:3178–3186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

